2015年3月23日
1.必须安装nodejs
2.安装cnpm用cnpm替代npm
地址:http://npm.taobao.org/
安装cnpm:
npm install -g cnpm --registry=https://registry.npm.taobao.org
3、用yarn替代npm
yarn的安装:
第一种方法:参考官方文档https://yarn.bootcss.com/
第二种方法:cnpm install -g yarn 或者 npm install -g yarn
4、搭建React开发环境的第一种方法(老-现在推荐):
https://reactjs.org/docs/create-a-new-react-app.html
1、必须要安装nodejs 注意:安装nodejs稳定版本 教程中的nodejs版本:v8.11.2 教程中的npm版本:v5.6.0
2.安装脚手架工具 (单文件组件项目生成工具) 只需要安装一次
npm install -g create-react-app / cnpm install -g create-react-app
3.创建项目 (可能创建多次)
找到项目要创建的目录:
create-react-app reactdemo
4.cd 到项目里面
cd reactdemo
npm start yarn start运行项目
npm run build yarn build 生成项目
5、搭建React的开发环境的第二种方法(新-未来推荐):
https://reactjs.org/docs/create-a-new-react-app.html
1、必须要安装nodejs 注意:安装nodejs稳定版本 教程中的nodejs版本:v8.11.2 教程中的npm版本:v5.6.0
2.安装脚手架工具并创建项目
找到项目要创建的目录执行:
npx create-react-app reactdemo
4.cd 到项目里面
cd reactdemo
npm start 运行项目(调试)
npm run build 生成项目(发布)
npx介绍:
npm v5.2.0引入的一条命令(npx),引入这个命令的目的是为了提升开发者使用包内提供的命令行工具的体验。
详情:
npx create-react-app reactdemo这条命令会临时安装 create-react-app 包,命令完成后create-react-app 会删掉,不会出现在 global 中。下次再执行,还是会重新临时安装。
npx 会帮你执行依赖包里的二进制文件。
再比如 npx http-server 可以一句话帮你开启一个静态服务器
posted @
2020-04-16 15:25 Terry Zou 阅读(339) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏
PostConstruct注释用于在完成依赖项注入以执行任何初始化之后需要执行的方法。必须在类投入使用之前调用此方法。
所有支持依赖注入的类都必须支持此注释。即使类没有请求注入任何资源,也必须调用使用PostConstruct注释的方法。
只有一个方法可以使用此批注进行批注。
应用PostConstruct注释的方法必须满足以下所有条件:除了拦截器之外,方法绝不能有任何参数,在这种情况下它采用Interceptor规范定义的InvocationContext对象。
在拦截器类上定义的方法必须具有以下签名之一:
void <METHOD>(InvocationContext)Object <METHOD>(InvocationContext)抛出异常注意:
PostConstruct拦截器方法不能抛出应用程序异常,但可以声明它抛出检查异常,包括java.lang.Exception,
如果相同的拦截器方法除了生命周期事件之外插入业务或超时方法。
如果PostConstruct拦截器方法返回一个值,容器将忽略它。
在非拦截器类上定义的方法必须具有以下签名:void <METHOD>()应用PostConstruct的方法可以是public,protected,package private或private。
除应用程序客户端外,该方法绝不能是静态的。
该方法可能是最终的。如果该方法抛出一个未经检查的异常,那么该类绝不能投入使用,除非EJB可以处理异常甚至从它们恢复的EJB
然后就会思考问题,这个注释是修饰初始化之后需要执行的方法,那么它和@Autowired、构造函数的执行顺序是什么呢?(当然注释中已经说明了PostConstruct注释用于在完成依赖项注入之后)
@Service
public class BeanA {
@Autowired
private BeanB beanB;
public BeanA() {
System.out.println("这是Bean A 的构造方法");
}
@PostConstruct
private void init() {
System.out.println("这是BeanA的 init 方法");
beanB.testB();
}
}
@Service
public class BeanB {
@PostConstruct
private void init() {
System.out.println("这是BeanB 的init 方法");
}
public BeanB() {
System.out.println("这是Bean B的 构造方法");
}
void testB() {
System.out.println("这是Bean B 的 testB 方法");
}
}
启动后输出:
这是Bean A 的构造方法
这是Bean B的 构造方法
这是BeanB 的init 方法
这是BeanA的 init 方法
这是Bean B 的 testB 方法
所以得到结论: 构造方法 > @Autowired > @PostConstruct
posted @
2020-04-09 15:29 Terry Zou 阅读(337) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏1、ApplicationContext
Spring的核心,Context我们通常解释为上下文环境。ApplicationContext则是应用的容器。 Spring把Bean(object)放在容器中,需要用就通过get方法取出来。在ApplicationContext接口的众多实现类中,有3个是我们经常用到的(见表1-1),并且使用这3个实现类也基本能满足我们Java EE应用开发中的绝大部分需求。
表1-1 ApplicationContext接口的常用实现类介绍
2、ApplicationEvent
是个抽象类,里面只有一个构造函数和一个长整型的timestamp。其源码如下
public abstract class ApplicationEvent extends EventObject {
/** use serialVersionUID from Spring 1.2 for interoperability */
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7099057708183571937L;
/** System time when the event happened */
private final long timestamp;
/**
* Create a new ApplicationEvent.
* @param source the object on which the event initially occurred (never {@code null})
*/
public ApplicationEvent(Object source) {
super(source);
this.timestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
/**
* Return the system time in milliseconds when the event happened.
*/
public final long getTimestamp() {
return this.timestamp;
}
}
3、ApplicationListener是一个接口,里面只有一个onApplicationEvent方法。如果在上下文中部署一个实现了ApplicationListener接口的bean,那么每当在一个ApplicationEvent发布到 ApplicationContext时,调用ApplicationContext.publishEvent()方法,这个bean得到通知。类似于Oberver设计模式。
其源码如下:
public interface ApplicationListener<E extends ApplicationEvent> extends EventListener {
/**
* Handle an application event.
* @param event the event to respond to
*/
void onApplicationEvent(E event);
}
下面举个例子
自定义事件NotifyEvent:
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent;
public class NotifyEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
private String email;
private String content;
public NotifyEvent(Object source){
super(source);
}
public NotifyEvent(Object source,String email,String content){
super(source);
this.email = email;
this.content = content;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
public void setContent(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
}
定义监听器NotifyListener:
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class NotifyListener implements ApplicationListener<NotifyEvent>{
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(NotifyEvent event) {
System.out.println("邮件地址:" + event.getEmail());
System.out.println("邮件内容:" + event.getContent());
}
}
单元测试类ListenerTest: import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = ServerLauncher.class, webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
public class ListenerTest {
@Autowired
private WebApplicationContext webApplicationContext;
@Test
public void testListener(){
NotifyEvent event = new NotifyEvent("object","abc@qq.com","This is the content");
webApplicationContext.publishEvent(event);
}
}
posted @
2020-04-09 14:47 Terry Zou 阅读(1315) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏之前用户使用的是3个注解注解他们的main类。分别是@Configuration,@EnableAutoConfiguration,@ComponentScan。由于这些注解一般都是一起使用,spring boot提供了一个统一的注解@SpringBootApplication。
@SpringBootApplication = (默认属性)@Configuration + @EnableAutoConfiguration + @ComponentScan。
@SpringBootApplication
public class ApplicationMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
分开解释@Configuration,@EnableAutoConfiguration,@ComponentScan。
1、@Configuration:提到@Configuration就要提到他的搭档@Bean。使用这两个注解就可以创建一个简单的spring配置类,可以用来替代相应的xml配置文件。
<beans>
<bean id = "car" class="com.test.Car">
<property name="wheel" ref = "wheel"></property>
</bean>
<bean id = "wheel" class="com.test.Wheel"></bean>
</beans>
相当于:
@Configuration
public class Conf {
@Bean
public Car car() {
Car car = new Car();
car.setWheel(wheel());
return car;
}
@Bean
public Wheel wheel() {
return new Wheel();
}
}
@Configuration的注解类标识这个类可以使用Spring IoC容器作为bean定义的来源。@Bean注解告诉Spring,一个带有@Bean的注解方法将返回一个对象,该对象应该被注册为在Spring应用程序上下文中的bean。
2、@EnableAutoConfiguration:能够自动配置spring的上下文,试图猜测和配置你想要的bean类,通常会自动根据你的类路径和你的bean定义自动配置。
3、@ComponentScan:会自动扫描指定包下的全部标有@Component的类,并注册成bean,当然包括@Component下的子注解@Service,@Repository,@Controller。
posted @
2020-04-09 09:10 Terry Zou 阅读(155) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏package com.zhihe.xqsh.utils;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import org.apache.http.HttpEntity;
import org.apache.http.HttpResponse;
import org.apache.http.HttpStatus;
import org.apache.http.HttpVersion;
import org.apache.http.NameValuePair;
import org.apache.http.client.ClientProtocolException;
import org.apache.http.client.HttpClient;
import org.apache.http.client.entity.UrlEncodedFormEntity;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpGet;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpPost;
import org.apache.http.conn.ClientConnectionManager;
import org.apache.http.conn.params.ConnManagerParams;
import org.apache.http.conn.params.ConnRouteParams;
import org.apache.http.conn.scheme.PlainSocketFactory;
import org.apache.http.conn.scheme.Scheme;
import org.apache.http.conn.scheme.SchemeRegistry;
import org.apache.http.conn.ssl.SSLSocketFactory;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.DefaultHttpClient;
import org.apache.http.impl.conn.tsccm.ThreadSafeClientConnManager;
import org.apache.http.impl.cookie.BasicClientCookie;
import org.apache.http.params.BasicHttpParams;
import org.apache.http.params.HttpConnectionParams;
import org.apache.http.params.HttpParams;
import org.apache.http.params.HttpProtocolParams;
import org.apache.http.util.EntityUtils;
import com.zhihe.xqsh.network.ServerErrorException;
import android.accounts.NetworkErrorException;
import android.annotation.SuppressLint;
import android.util.Log;
public class CustomerHttpClient {
private static final String TAG = CustomerHttpClient.class.getSimpleName();
private static DefaultHttpClient customerHttpClient;
private CustomerHttpClient() {
}
public static synchronized HttpClient getHttpClient() {
if (null == customerHttpClient) {
HttpParams params = new BasicHttpParams();
// 设置�?��基本参数
HttpProtocolParams.setVersion(params, HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1);
HttpProtocolParams.setContentCharset(params, "UTF-8");
HttpProtocolParams.setUseExpectContinue(params, true);
HttpProtocolParams.setUserAgent(params, "Mozilla/5.0(Linux;U;Android 2.2.1;en-us;Nexus One Build.FRG83) "
+ "AppleWebKit/553.1(KHTML,like Gecko) Version/4.0 Mobile Safari/533.1");
// 超时设置
/* 从连接池中取连接的超时时�?*/
ConnManagerParams.setTimeout(params, 2000);
ConnManagerParams.setMaxTotalConnections(params, 800);
/* 连接超时 */
HttpConnectionParams.setConnectionTimeout(params, 5000);
/* 请求超时 */
HttpConnectionParams.setSoTimeout(params, 10000);
// 设置我们的HttpClient支持HTTP和HTTPS两种模式
SchemeRegistry schReg = new SchemeRegistry();
schReg.register(new Scheme("http", PlainSocketFactory.getSocketFactory(), 80));
schReg.register(new Scheme("https", SSLSocketFactory.getSocketFactory(), 443));
// 使用线程安全的连接管理来创建HttpClient
ClientConnectionManager conMgr = new ThreadSafeClientConnManager(params, schReg);
// �?��连接数:ConnManagerParams.setMaxTotalConnections(params, 50);
customerHttpClient = new DefaultHttpClient(conMgr, params);
}
return customerHttpClient;
}
/**
* 以get方式提交数据
*
* @param url 提交地址
* @param params 参数
* @return 响应结果
* @throws ServerErrorException 请求失败
* @throws NetworkErrorException 连接失败
*/
public static String get(String url, String params) throws ServerErrorException, NetworkErrorException {
int tryTimes = 0;
NullPointerException ex;
do {
try {
return tryGet(url, params);
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
ex = e;
tryTimes++;
}
} while (tryTimes < 3);
throw ex;
}
/**
* 以get方式提交数据
*
* @param url 提交地址
* @param params 参数
* @return 响应结果
* @throws ServerErrorException 请求失败
* @throws NetworkErrorException 连接失败
*/
public static String tryGet(String url, String params) throws ServerErrorException, NetworkErrorException {
try {
HttpGet request = new HttpGet(url + params);
/*if (LotteryApplication.isCmwap()) {
org.apache.http.HttpHost proxy = new org.apache.http.HttpHost("10.0.0.172", 80, "http");
HttpParams httpParams = new BasicHttpParams();
ConnRouteParams.setDefaultProxy(httpParams, proxy);
request.setParams(httpParams);
}*/
HttpClient client = getHttpClient();
HttpResponse response = client.execute(request);
if (response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() != HttpStatus.SC_OK) {
throw new ServerErrorException("��������æ�����Ժ�����");
}
HttpEntity resEntity = response.getEntity();
String result = (resEntity == null) ? null : EntityUtils.toString(resEntity, "UTF-8");
return result;
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
logw(e.getMessage());
return null;
} catch (ClientProtocolException e) {
logw(e.getMessage());
return null;
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new NetworkErrorException("���Ӳ��ɹ���������������", e);
}
}
private static void logw(String string) {
if (string != null) {
Log.w(TAG, string);
}
}
/**
* 以post方式提交数据
*
* @param url 提交地址
* @param params 参数
* @return 响应结果
* @throws ServerErrorException 请求失败
* @throws NetworkErrorException 连接失败
*/
public static String post(String url, List<NameValuePair> params) throws ServerErrorException, NetworkErrorException {
return post(url, params, null);
}
/**
* 以post方式提交数据
*
* @param url 提交地址
* @param params 参数
* @param soTimeout 响应超时时间,单位毫�?
* @return 响应结果
* @throws ServerErrorException 请求失败
* @throws NetworkErrorException 连接失败
*/
public static String post(String url, List<NameValuePair> params, int soTimeout) throws ServerErrorException,
NetworkErrorException {
HttpParams httpParams;
if (soTimeout <= 0) {
httpParams = null;
} else {
httpParams = new BasicHttpParams();
HttpConnectionParams.setSoTimeout(httpParams, soTimeout);
}
return post(url, params, httpParams);
}
/**
* 以post方式提交数据
*
* @param url 提交地址
* @param params 参数
* @param httpParams http参数
* @return 响应结果
* @throws ServerErrorException 请求失败
* @throws NetworkErrorException 连接失败
*/
public static String post(String url, List<NameValuePair> params, HttpParams httpParams) throws ServerErrorException,
NetworkErrorException {
int tryTimes = 0;
NullPointerException ex;
do {
try {
return tryPost(url, params, httpParams);
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
ex = e;
tryTimes++;
}
} while (tryTimes < 3);
throw ex;
}
/**
* 以post方式提交数据
*
* @param url 提交地址
* @param params 参数
* @param httpParams http参数
* @return 响应结果
* @throws ServerErrorException 请求失败
* @throws NetworkErrorException 连接失败
*/
public static String tryPost(String url, List<NameValuePair> params, HttpParams httpParams) throws ServerErrorException,
NetworkErrorException {
try {
HttpPost request = new HttpPost(url);
if (params != null && params.size() > 0) {
request.setEntity(new UrlEncodedFormEntity(params, "UTF-8"));
}
// if (LotteryApplication.isCmwap()) {
// org.apache.http.HttpHost proxy = new org.apache.http.HttpHost("10.0.0.172", 80, "http");
// if (httpParams == null)
// httpParams = new BasicHttpParams();
// ConnRouteParams.setDefaultProxy(httpParams, proxy);
// }
if (httpParams != null)
request.setParams(httpParams);
//Log.v("CS", params.toString());
HttpClient client = getHttpClient();
HttpResponse response = client.execute(request);
if (response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() != HttpStatus.SC_OK) {
//Log.v("CS", params.toString());
//Log.v("CS", response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() + "");
request.abort();
throw new ServerErrorException("��������æ�����Ժ�����");
}
if (response.getStatusLine ().getStatusCode () != 200) {
request.abort(); //�ж�����,���������Կ�ʼ��һ������
return null;
}
HttpEntity resEntity = response.getEntity();
String result = (resEntity == null) ? null : EntityUtils.toString(resEntity, "UTF-8");
//Log.v("CS", params.toString() + "||||" + result);
return result;
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
logw(e.getMessage());
return null;
} catch (ClientProtocolException e) {
logw(e.getMessage());
return null;
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new NetworkErrorException(e.getMessage(), e);
//throw new NetworkErrorException("连接不成功,请检查网络设�?, e);
}
}
@SuppressLint("SdCardPath")
public static String download(String url) throws ServerErrorException, NetworkErrorException {
try {
//Log.i("http-download", url);
HttpPost request = new HttpPost(url);
HttpClient client = getHttpClient();
HttpResponse response = client.execute(request);
if (response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() != HttpStatus.SC_OK) {
throw new ServerErrorException("��������æ�����Ժ�����");
}
HttpEntity entity = response.getEntity();
InputStream is = entity.getContent();
if (is == null)
throw new ServerErrorException("stream is null ");
String fileExt = url.substring(url.lastIndexOf(".") + 1, url.length()).toLowerCase();
String fileName = url.substring(url.lastIndexOf("/") + 1, url.lastIndexOf("."));
File tempFile = new File("/sdcard/" + fileName + "." + fileExt);
if (!tempFile.exists())
tempFile.createNewFile();
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(tempFile);
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int ch;
while ((ch = is.read(buf)) != -1) {
fileOutputStream.write(buf, 0, ch);
}
fileOutputStream.flush();
fileOutputStream.close();
return tempFile.getAbsolutePath();
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
logw(e.getMessage());
return null;
} catch (ClientProtocolException e) {
logw(e.getMessage());
return null;
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new NetworkErrorException(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
/**
* 清空cookie
*/
public static void clearCookie() {
if (customerHttpClient != null)
customerHttpClient.getCookieStore().clear();
}
/**
* 清除指定cookie
*
* @param name cookie名称
*/
public static void clearCookie(String name) {
if (customerHttpClient == null)
return;
BasicClientCookie expiredCookie = new BasicClientCookie(name, "null");
expiredCookie.setExpiryDate(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis() - 1000));
customerHttpClient.getCookieStore().addCookie(expiredCookie);
}
}
posted @
2015-07-13 22:10 Terry Zou 阅读(302) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏
http://yunpan.cn/ccdbTgQaYa4U7
posted @
2015-07-13 11:04 Terry Zou 阅读(150) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏private Drawable img_time_filter,img_time_filter_selected ;
//过滤器TextView中显示的图片
img_time_filter = getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.time_filter);
//调用setCompoundDrawables时,必须调用Drawable.setBounds()方法,否则图片不显示
img_time_filter.setBounds(0, 0, img_time_filter.getMinimumWidth(), img_time_filter.getMinimumHeight());
img_time_filter_selected = getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.time_filter_selected);
img_time_filter_selected.setBounds(0, 0, img_time_filter_selected.getMinimumWidth(), img_time_filter_selected.getMinimumHeight());
tv_filterTime.setCompoundDrawables(img_time_filter_selected, null, null, null);
tv_filterTime.setTextColor(getResources().getColor(R.color.white));
rl_filterTime.setBackgroundColor(getResources().getColor(R.color.red));
tv_filterTime.setCompoundDrawables(img_time_filter, null, null, null);
rl_filterTime.setBackgroundColor(getResources().getColor(R.color.white));
lv_filterTime.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);
posted @
2015-07-09 00:04 Terry Zou 阅读(236) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="@color/white"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<com.baidu.mapapi.map.MapView
android:id="@+id/bmapView_routePlanActivity"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:clickable="true" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:background="@drawable/common_title_back"
android:gravity="center"
android:padding="5dp" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/button_transit_routePlan"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:drawableLeft="@drawable/ic_bus"
android:padding="5dp"
android:background="@drawable/selector_white_gray"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:layout_weight="1.0"
android:onClick="SearchButtonProcess"
android:text="公交" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button_drive_routePlan"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:drawableLeft="@drawable/ic_drive"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:layout_weight="1.0"
android:padding="5dp"
android:background="@drawable/selector_white_gray"
android:onClick="SearchButtonProcess"
android:text="驾车" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button_walk_routePlan"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:drawableLeft="@drawable/ic_walk"
android:layout_weight="1.0"
android:padding="5dp"
android:background="@drawable/selector_white_gray"
android:onClick="SearchButtonProcess"
android:text="步行" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/linearLayout_node_routePlan"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_marginBottom="10dip"
android:visibility="gone"
android:gravity="bottom|center_horizontal" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/button_pre_routePlan"
android:layout_width="60dp"
android:layout_height="30dp"
android:layout_marginRight="2dip"
android:background="@drawable/pre_"
android:onClick="nodeClick" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button_next_routePlan"
android:layout_width="60dp"
android:layout_height="30dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="2dip"
android:background="@drawable/next_"
android:onClick="nodeClick" />
</LinearLayout>
</FrameLayout>
posted @
2015-07-08 23:57 Terry Zou|
编辑 收藏<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/estate_linear"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="35dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="@drawable/border_rounded_gray_white"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical"
android:gravity="center_vertical"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<ImageButton
android:id="@+id/object_btn_search"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="8dp"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical|right"
android:background="@drawable/btn_search"
android:contentDescription="@null"
android:scaleType="fitXY" />
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="1dp"
android:layout_height="33dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="8dp"
android:background="@color/color_line" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/object_et_content"
style="@style/StringSearchText"
android:layout_gravity="left|center_vertical"
android:layout_marginLeft="2dp"
android:layout_marginRight="8dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="@null"
android:hint="@string/tip_search_hint"
android:imeOptions="actionSend"
android:singleLine="true"
android:textCursorDrawable="@null"
android:textColorHint="#626463" />
<ImageButton
android:id="@+id/object_btn_del"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="right|center_vertical"
android:layout_marginRight="10dp"
android:background="@drawable/ic_clear" />
</LinearLayout>



border_rounded_gray_white.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<layer-list xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" >
<!-- 连框颜色值 -->
<item>
<shape>
<solid android:color="@color/bg_gray" />
<corners
android:bottomLeftRadius="3dp"
android:bottomRightRadius="3dp"
android:topLeftRadius="3dp"
android:topRightRadius="3dp" />
</shape>
</item>
<!-- 主体背景颜色值 -->
<item
android:bottom="1dp"
android:left="1dp"
android:right="1dp"
android:top="1dp">
<shape>
<solid android:color="@color/white" />
<corners
android:bottomLeftRadius="3dp"
android:bottomRightRadius="3dp"
android:topLeftRadius="3dp"
android:topRightRadius="3dp" />
</shape>
</item>
</layer-list>
<style name="StringSearchText">
<item name="android:textSize">14dp</item>
<item name="android:layout_width">wrap_content</item>
<item name="android:layout_height">wrap_content</item>
<item name="android:textColor">@android:color/black</item>
</style>
btn_search.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<selector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<!-- 没有焦点时的背景图片 -->
<item android:drawable="@drawable/ic_search_normal" android:state_window_focused="false"/>
<!-- 非触摸模式下获得焦点并单击时的背景图片 -->
<item android:drawable="@drawable/ic_search_pressed" android:state_focused="true" android:state_pressed="true"/>
<!-- 触摸模式下单击时的背景图片 -->
<item android:drawable="@drawable/ic_search_pressed" android:state_focused="false" android:state_pressed="true"/>
<!-- 选中时的图片背景 -->
<item android:drawable="@drawable/ic_search_pressed" android:state_selected="true"/>
<!-- 获得焦点时的图片背景 -->
<item android:drawable="@drawable/ic_search_pressed" android:state_focused="true"/>
<!-- 默认图片背景 -->
<item android:drawable="@drawable/ic_search_normal"/>
</selector>
<color name="color_line">#bebebe</color>
private TextWatcher textWatcher = new TextWatcher() {
@Override
public void beforeTextChanged(CharSequence s, int start, int count,
int after) {
}
@Override
public void onTextChanged(CharSequence s, int start, int before,
int count) {
}
@Override
public void afterTextChanged(Editable s) {
mKeywords = tv_keyword.getText().toString();
AgUtils.log(TAG+"mKeywords:"+mKeywords, 4);
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(mKeywords)) {
object_btn_del.setVisibility(View.GONE);
} else {
object_btn_del.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
searchIndexListInfo();
}
}
};
tv_keyword.addTextChangedListener(textWatcher);
posted @
2015-07-08 23:55 Terry Zou|
编辑 收藏转载:http://www.cnblogs.com/allenzheng/archive/2013/04/28/3050065.html
当应用运行起来后就会开启一条线程,线程中会运行一个任务栈,当Activity实例创建后就会放入任务栈中。Activity启动模式的设置在AndroidManifest.xml文件中,通过配置Activity的属性android:launchMode=""设置。
1. Standared模式(默认)
我们平时直接创建的Activity都是这种模式的Activity,这种模式的Activity的特点是:只要你创建了Activity实例,一旦激活该Activity,则会向任务栈中加入新创建的实例,退出Activity则会在任务栈中销毁该实例。
2. SingleTop模式
这种模式会考虑当前要激活的Activity实例在任务栈中是否正处于栈顶,如果处于栈顶则无需重新创建新的实例,会重用已存在的实例,否则会在任务栈中创建新的实例。
3. SingleTask模式
如果任务栈中存在该模式的Activity实例,则把栈中该实例以上的Activity实例全部移除,调用该实例的newInstance()方法重用该Activity,使该实例处於栈顶位置,否则就重新创建一个新的Activity实例。
4. SingleInstance模式
当该模式Activity实例在任务栈中创建后,只要该实例还在任务栈中,即只要激活的是该类型的Activity,都会通过调用实例的newInstance()方法重用该Activity,此时使用的都是同一个Activity实例,它都会处于任务栈的栈顶。此模式一般用于加载较慢的,比较耗性能且不需要每次都重新创建的Activity。
posted @
2015-06-24 18:10 Terry Zou 阅读(498) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏
摘要: android中跨进程通讯的4种方式
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/sevenyuan/archive/2013/03/22/2975122.html由于android系统中应用程序之间不能共享内存。因此,在不同应用程序之间交互数据(跨进程通讯)就稍微麻烦一些。在android SDK中提供了4种用于跨进程通讯的方式。这4种方式正好对应于android系统中4种应用...
阅读全文
posted @
2015-06-24 17:28 Terry Zou 阅读(526) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏Android 手机上的应用一般情况下都在一个进程中运行。
但是,也可以指定Activity或者Service在Remote 进程中执行。多数情况下,只有在用户认为应用退出后还需要继续后台长期运行的应用,才需要这样做。此时,该应用有两个进程。
还有一种hack的方式,在apk中通过调用命令行来启动另外的进程。此种方式用户不可见,也不安全。不提倡。
posted @
2015-06-24 17:12 Terry Zou 阅读(570) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏官网帮助文档链接:
http://developer.android.com/guide/components/fragments.html
主要看两张图,和跑代码
一,Fragment的生命周

二,与Activity生命周期的对比

场景演示 : 切换到该Fragment
11-29 14:26:35.095: D/AppListFragment(7649): onAttach
11-29 14:26:35.095: D/AppListFragment(7649): onCreate
11-29 14:26:35.095: D/AppListFragment(7649): onCreateView
11-29 14:26:35.100: D/AppListFragment(7649): onActivityCreated
11-29 14:26:35.120: D/AppListFragment(7649): onStart
11-29 14:26:35.120: D/AppListFragment(7649): onResume
屏幕灭掉:
11-29 14:27:35.185: D/AppListFragment(7649): onPause
11-29 14:27:35.205: D/AppListFragment(7649): onSaveInstanceState
11-29 14:27:35.205: D/AppListFragment(7649): onStop
屏幕解锁
11-29 14:33:13.240: D/AppListFragment(7649): onStart
11-29 14:33:13.275: D/AppListFragment(7649): onResume
切换到其他Fragment:
11-29 14:33:33.655: D/AppListFragment(7649): onPause
11-29 14:33:33.655: D/AppListFragment(7649): onStop
11-29 14:33:33.660: D/AppListFragment(7649): onDestroyView
切换回本身的Fragment:
11-29 14:33:55.820: D/AppListFragment(7649): onCreateView
11-29 14:33:55.825: D/AppListFragment(7649): onActivityCreated
11-29 14:33:55.825: D/AppListFragment(7649): onStart
11-29 14:33:55.825: D/AppListFragment(7649): onResume
回到桌面
11-29 14:34:26.590: D/AppListFragment(7649): onPause
11-29 14:34:26.880: D/AppListFragment(7649): onSaveInstanceState
11-29 14:34:26.880: D/AppListFragment(7649): onStop
回到应用
11-29 14:36:51.940: D/AppListFragment(7649): onStart
11-29 14:36:51.940: D/AppListFragment(7649): onResume
退出应用
11-29 14:37:03.020: D/AppListFragment(7649): onPause
11-29 14:37:03.155: D/AppListFragment(7649): onStop
11-29 14:37:03.155: D/AppListFragment(7649): onDestroyView
11-29 14:37:03.165: D/AppListFragment(7649): onDestroy
11-29 14:37:03.165: D/AppListFragment(7649): onDetach
比Activity多了一些生命周期,完整和Activity对接上,大家好好利用。
转载:http://blog.csdn.net/forever_crying/article/details/8238863/
posted @
2015-06-24 16:05 Terry Zou 阅读(459) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏ANR(Application Not Responding)
ANR定义:在Android上,如果你的应用程序有一段时间响应不够灵敏,系统会向用户显示一个对话框,这个对话框称作应用程序无响应对话框(ANR:Application Not Responding),用户可以选择“等待”让应用程序继续运行,也可以选择“强制关闭”。所以一个顺畅合理的应用程序不会出现ANR,而让用户处理这个对话框。因此,在程序里对响应性能的设计很重要,这样系统不会显示ANR给用户。
默认情况下,Android的Activity执行时间为5s,BroadcastReceiver的最长执行时间为10s.
第一,什么会引发ANR
在Android里,应用程序响应由Activity Manager和WindowManager系统服务监视的,当它监听到一下一种情况时,Android就会针对特定的应用程序显示ANR:
1).在5秒内没有响应输入事件(例如,按键按下,屏幕触摸)
2).BroadcastReceiver在10秒内没有执行完毕
造成以上两点多原因有很多,比如在主线程中做非常耗时的操作,比如下载,IO异常等。
潜在的耗时操作,例如网络或数据库操作或者高耗时的计算如改变位图尺寸,这些操作应该放在子线程中(或者以数据库为例,通过异步请求的方式)来完成,然而,不是说你的主线程阻塞在那里等待子线程来完成--也不用调用Thread.wait()或Thread.sleep();替代的方法是主线程需要为子线程提供一个handler,以便完成时能够交给主线程,以这种方式设计你的应用程序,将能保证你的主线程保持对输入的响应性并能避免由于5秒输入事件的超时引发的ANR对话框。
第二,如何避免ANR
1.运行在主线程里的任何方法都尽可能少做事情。特别是,Activity应该在它的关键生命周期方法(如onCreate()和onResume())里尽可能少的去做创建操作。(可以采用重新开启子线程的方式,然后使用Handler+Message的方式做一些操作,比如更新主线程中的ui等)
2.应用程序应该避免在BroadcastReceiver里做耗时的操作或计算。但不再是在子线程里做这些任务(因为 BroadcastReceiver的生命周期短),替代的是,如果响应Intent广播需要执行一个耗时的动作的话,应用程序应该启动一个 Service。(此处需要注意的是可以在广播接受者中启动Service,但是却不可以在Service中启动broadcasereciver,关于原因后续会有介绍,此处不是本文重点)
3.避免在Intent Receiver里启动一个Activity,因为它会创建一个新的画面,并从当前用户正在运行的程序上抢夺焦点。如果你的应用程序在响应Intent广 播时需要向用户展示什么,你应该使用Notification Manager来实现。
总结:anr异常也是在程序中自己经常遇到的问题,主要的解决办法自己最常用的就是不要在主线程中做耗时的操作,而应放在子线程中来实现,比如采用Handler+mesage的方式,或者是有时候需要做一些和网络相互交互的耗时操作就采用asyntask异步任务的方式(它的底层其实Handler+mesage有所区别的是它是线程池)等,在主线程中更新UI。
posted @
2015-06-24 16:00 Terry Zou 阅读(328) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏
摘要: String string="
欢迎你来到的
jack
的
android
使用技术总结
";
TextV
iew info2=(TextView)super.findV
iewById(R.id.info); ...
阅读全文
posted @
2015-06-15 14:21 Terry Zou 阅读(239) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏
摘要: 开发自定义控件的步骤:
1、了解View的工作原理
2、 编写继承自View的子类
3、 为自定义View类增加属性
4、 绘制控件
5、 响应用户消息
6 、自定义回调函数
一、View结构原理
Android系统的视图结构的设计也采用了组合模式,即View作为所有图形的基类,Viewgroup对View继承...
阅读全文
posted @
2015-05-19 17:29 Terry Zou 阅读(389) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏
摘要: Android 管理Fragments
FragmentManager
为了管理Activity中的fragments,需要使...
阅读全文
posted @
2015-05-18 18:28 Terry Zou 阅读(443) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏|
java.version |
Java 运行时环境版本 |
|
java.vendor |
Java 运行时环境供应商 |
|
java.vendor.url |
Java 供应商的 URL |
|
java.home |
Java 安装目录 |
|
java.vm.specification.version |
Java 虚拟机规范版本 |
|
java.vm.specification.vendor |
Java 虚拟机规范供应商 |
|
java.vm.specification.name |
Java 虚拟机规范名称 |
|
java.vm.version |
Java 虚拟机实现版本 |
|
java.vm.vendor |
Java 虚拟机实现供应商 |
|
java.vm.name |
Java 虚拟机实现名称 |
|
java.specification.version |
Java 运行时环境规范版本 |
|
java.specification.vendor |
Java 运行时环境规范供应商 |
|
java.specification.name |
Java 运行时环境规范名称 |
|
java.class.version |
Java 类格式版本号 |
|
java.class.path |
Java 类路径 |
|
java.library.path |
加载库时搜索的路径列表 |
|
java.io.tmpdir |
默认的临时文件路径 |
|
java.compiler |
要使用的 JIT 编译器的名称 |
|
java.ext.dirs |
一个或多个扩展目录的路径 |
|
os.name |
操作系统的名称 |
|
os.arch |
操作系统的架构 |
|
os.version |
操作系统的版本 |
|
file.separator |
文件分隔符(在 UNIX 系统中是“/”) |
|
path.separator |
路径分隔符(在 UNIX 系统中是“:”) |
|
line.separator |
行分隔符(在 UNIX 系统中是“/n”) |
|
user.name |
用户的账户名称 |
|
user.home |
用户的主目录 |
|
user.dir |
用户的当前工作目录 |
StringBuffer response = new StringBuffer();while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) { response.append(line).append( System.getProperty("line.separator"));}
public class SystemProperty {
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println("java_vendor:" + System.getProperty("java.vendor"));
System.out.println("java_vendor_url:"
+ System.getProperty("java.vendor.url"));
System.out.println("java_home:" + System.getProperty("java.home"));
System.out.println("java_class_version:"
+ System.getProperty("java.class.version"));
System.out.println("java_class_path:"
+ System.getProperty("java.class.path"));
System.out.println("os_name:" + System.getProperty("os.name"));
System.out.println("os_arch:" + System.getProperty("os.arch"));
System.out.println("os_version:" + System.getProperty("os.version"));
System.out.println("user_name:" + System.getProperty("user.name"));
System.out.println("user_home:" + System.getProperty("user.home"));
System.out.println("user_dir:" + System.getProperty("user.dir"));
System.out.println("java_vm_specification_version:"
+ System.getProperty("java.vm.specification.version"));
System.out.println("java_vm_specification_vendor:"
+ System.getProperty("java.vm.specification.vendor"));
System.out.println("java_vm_specification_name:"
+ System.getProperty("java.vm.specification.name"));
System.out.println("java_vm_version:"
+ System.getProperty("java.vm.version"));
System.out.println("java_vm_vendor:"
+ System.getProperty("java.vm.vendor"));
System.out
.println("java_vm_name:" + System.getProperty("java.vm.name"));
System.out.println("java_ext_dirs:"
+ System.getProperty("java.ext.dirs"));
System.out.println("file_separator:"
+ System.getProperty("file.separator"));
System.out.println("path_separator:"
+ System.getProperty("path.separator"));
System.out.println("line_separator:"
+ System.getProperty("line.separator"));
}
转载:http://blog.csdn.net/kongqz/article/details/3987198
posted @
2015-05-15 09:33 Terry Zou 阅读(416) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏
注意上面的双引号,何为“容易”?言下之意就是该activity还没有被销毁,而仅仅是一种可能性。这种可能性有哪些?通过重写一个activity的所有生命周期的onXXX方法,包括onSaveInstanceState和onRestoreInstanceState方法,我们可以清楚地知道当某个activity(假定为activity A)显示在当前task的最上层时,其onSaveInstanceState方法会在什么时候被执行,有这么几种情况:
1、当用户按下HOME键时。
这是显而易见的,系统不知道你按下HOME后要运行多少其他的程序,自然也不知道activity A是否会被销毁,故系统会调用onSaveInstanceState,让用户有机会保存某些非永久性的数据。以下几种情况的分析都遵循该原则
2、长按HOME键,选择运行其他的程序时。
3、按下电源按键(关闭屏幕显示)时。
4、从activity A中启动一个新的activity时。
5、屏幕方向切换时,例如从竖屏切换到横屏时。
在屏幕切换之前,系统会销毁activity A,在屏幕切换之后系统又会自动地创建activity A,所以onSaveInstanceState一定会被执行。
总而言之,onSaveInstanceState的调用遵循一个重要原则,即当系统“未经你许可”时销毁了你的activity,则onSaveInstanceState会被系统调用,这是系统的责任,因为它必须要提供一个机会让你保存你的数据(当然你不保存那就随便你了)。
至于onRestoreInstanceState方法,需要注意的是,onSaveInstanceState方法和onRestoreInstanceState方法“不一定”是成对的被调用的,onRestoreInstanceState被调用的前提是,activity A“确实”被系统销毁了,而如果仅仅是停留在有这种可能性的情况下,则该方法不会被调用,例如,当正在显示activity A的时候,用户按下HOME键回到主界面,然后用户紧接着又返回到activity A,这种情况下activity A一般不会因为内存的原因被系统销毁,故activity A的onRestoreInstanceState方法不会被执行。
另外,onRestoreInstanceState的bundle参数也会传递到onCreate方法中,你也可以选择在onCreate方法中做数据还原。 转载:http://gundumw100.iteye.com/blog/1115080
posted @
2015-05-11 10:34 Terry Zou 阅读(361) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏Android中常常使用shape来定义控件的一些显示属性,今天看了一些shape的使用,对shape有了大体的了解,稍作总结:
先看下面的代码:
<shape>
<!-- 实心 -->
<solid android:color="#ff9d77"/>
<!-- 渐变 -->
<gradient
android:startColor="#ff8c00"
android:endColor="#FFFFFF"
android:angle="270" />
<!-- 描边 -->
<stroke
android:width="2dp"
android:color="#dcdcdc" />
<!-- 圆角 -->
<corners
android:radius="2dp" />
<padding
android:left="10dp"
android:top="10dp"
android:right="10dp"
android:bottom="10dp" />
</shape>
solid:实心,就是填充的意思
android:color指定填充的颜色
gradient:渐变
android:startColor和android:endColor分别为起始和结束颜色,ndroid:angle是渐变角度,必须为45的整数倍。
另外渐变默认的模式为android:type="linear",即线性渐变,可以指定渐变为径向渐变,android:type="radial",径向渐变需要指定半径android:gradientRadius="50"。
stroke:描边
android:width="2dp" 描边的宽度,android:color 描边的颜色。
我们还可以把描边弄成虚线的形式,设置方式为:
android:dashWidth="5dp"
android:dashGap="3dp"
其中android:dashWidth表示'-'这样一个横线的宽度,android:dashGap表示之间隔开的距离。
corners:圆角
android:radius为角的弧度,值越大角越圆。
我们还可以把四个角设定成不同的角度,方法为:
<corners
android:topRightRadius="20dp" 右上角
android:bottomLeftRadius="20dp" 右下角
android:topLeftRadius="1dp" 左上角
android:bottomRightRadius="0dp" 左下角
/>
这里有个地方需要注意,bottomLeftRadius是右下角,而不是左下角,这个有点郁闷,不过不影响使用,记得别搞错了就行。
还有网上看到有人说设置成0dp无效,不过我在测试中发现是可以的,我用的是2.2,可能修复了这个问题吧,如果无效的话那就只能设成1dp了。
padding:间隔
这个就不用多说了,XML布局文件中经常用到。
大体的就是这样,以下是一个使用的具体示例:用在Selector中作为Button的背景,分别定义了按钮的一般状态、获得焦点状态和按下时的状态,具体代码如下:
main.xml:
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="TestShapeButton"
android:background="@drawable/button_selector"
/>
button_selector.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<selector
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<item android:state_pressed="true" >
<shape>
<!-- 渐变 -->
<gradient
android:startColor="#ff8c00"
android:endColor="#FFFFFF"
android:type="radial"
android:gradientRadius="50" />
<!-- 描边 -->
<stroke
android:width="2dp"
android:color="#dcdcdc"
android:dashWidth="5dp"
android:dashGap="3dp" />
<!-- 圆角 -->
<corners
android:radius="2dp" />
<padding
android:left="10dp"
android:top="10dp"
android:right="10dp"
android:bottom="10dp" />
</shape>
</item>
<item android:state_focused="true" >
<shape>
<gradient
android:startColor="#ffc2b7"
android:endColor="#ffc2b7"
android:angle="270" />
<stroke
android:width="2dp"
android:color="#dcdcdc" />
<corners
android:radius="2dp" />
<padding
android:left="10dp"
android:top="10dp"
android:right="10dp"
android:bottom="10dp" />
</shape>
</item>
<item>
<shape>
<solid android:color="#ff9d77"/>
<stroke
android:width="2dp"
android:color="#fad3cf" />
<corners
android:topRightRadius="5dp"
android:bottomLeftRadius="5dp"
android:topLeftRadius="0dp"
android:bottomRightRadius="0dp"
/>
<padding
android:left="10dp"
android:top="10dp"
android:right="10dp"
android:bottom="10dp" />
</shape>
</item>
</selector>
运行效果如下图:
一般状态:

获得焦点状态:

按下状态:

转载:http://kofi1122.blog.51cto.com/2815761/521605/
posted @
2015-04-18 10:41 Terry Zou 阅读(289) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏
摘要: 所谓自定义控件(或称组件)也就是编写自己的控件类型,而非Android中提供的标准的控件,如TextView,CheckBox等等.不过自定义的控件一般也都是从标准控件继承来的,或者是多种控件组合,或者是对标准控件的属性进行改变而得到的自己满意的控件.
自定义控件可能会有很多种方法,这里只介绍我要介绍的方法.
&nb...
阅读全文
posted @
2015-04-14 10:53 Terry Zou 阅读(348) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏在Android的联机文档中,有对Activity的简单介绍,现在通过编写代码对Activity的启动模式做一个深入的理解。
在配置文件AndroidManifest.xml中,activity元素的android:launchMode属性用来配置对应Activity的启动模式,目前有以下四种启动模式:
1.standard
2.singleTop
3.singleTask
4.singleInstance
如果不对Activity设置启动模式,默认就是standard模式
一、standard
请看以下代码,实现了一个Activity :
public class A_Activity extends Activity {
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
TextView textView=new TextView(this);
textView.setText(this+"");//这里用于打印当前Activity的hashcode,可以此判断Activity实例是不是同一个对象
Button button=new Button(this);
button.setText("Go next activity");
button.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener(){
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Intent intent=new Intent();
intent.setClass(A_Activity.this, A_Activity.class);//说明发出Intent与启动的Activity都是A_Activity的实例
startActivity(intent);
}
});
LinearLayout layout=new LinearLayout(this);
layout.setOrientation(LinearLayout.VERTICAL);
layout.addView(textView);
layout.addView(button);
setContentView(layout);
}
}
运行之,请看下图:

点击button后,注意看第一行的textView
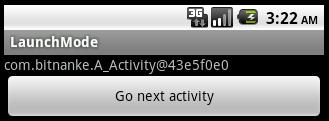
由此可知,生成了新的A_Activity对象,这时我们按回退键,就会依次回到之前的Activity。点击button的过程就是压栈的过程,在standard模式下,就会不断生成新的Activity对象
二、singleTop
singleTop和standard模式都会将intent发送给新的Activity实例,不同的是,如果创建Intent的时候栈顶有要创建的singleTop模式下的Activity实例,则将Intent发送给该实例,不会再创建Activity的新实例。
还是使用之前的代码,只是设置A_Activity的启动模式为singleTop:android:launchMode="singleTop",运行之,请看下图:

这个时候我们无论点击多少次button,textView都显示同一个Activity实例,按回退键时会直接退出程序,表明在singleTop模式下,如果在栈顶存在Intent中那个目标Activity的实例,就不会创建新的实例,而直接使用栈顶的对象,对于资源有限的移动设备来说,也是有实际意义的。
如果是在不同Activity之间跳转,就会跟standard模式的情形一样,请看下面代码:
public class A_Activity extends Activity {
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
TextView textView=new TextView(this);
textView.setText(this+"");
Button button=new Button(this);
button.setText("Go B_Activity");
button.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener(){
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Intent intent=new Intent();
intent.setClass(A_Activity.this, B_Activity.class);//从A跳转到B
startActivity(intent);
}
});
LinearLayout layout=new LinearLayout(this);
layout.setOrientation(LinearLayout.VERTICAL);
layout.addView(textView);
layout.addView(button);
setContentView(layout);
}
}
public class B_Activity extends Activity {
/**<li>Description: </li>
*
* @param savedInstanceState
* @see android.app.Activity#onCreate(android.os.Bundle)
*/
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
TextView textView=new TextView(this);
textView.setText(this+"");
Button button=new Button(this);
button.setText("Go A_Activity");
button.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener(){
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Intent intent=new Intent();
intent.setClass(B_Activity.this, A_Activity.class);//从B跳转到A
startActivity(intent);
}
});
LinearLayout layout=new LinearLayout(this);
layout.setOrientation(LinearLayout.VERTICAL);
layout.addView(textView);
layout.addView(button);
setContentView(layout);
}
}
运行后,如下图:
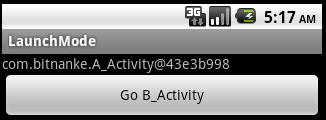
点击button后:
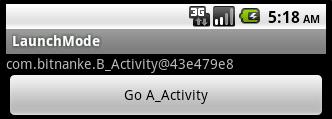
再点击button后:
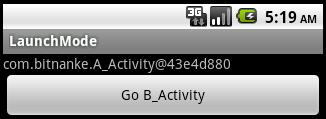
这样每次都会创建目标Activity的新实例,因为在跳转时,处于栈顶的对象不是目标Activity的实例
三、singleTask
singleTask模式只能创建一个实例,当发送一个Intent,目标Activity为singleTask模式时,系统会检查栈里面是否已经有该Activity的实例,如果有就直接将Intent发送给它,还是使用(二)中的代码,将A_Activity启动模式设置为singleTask,B_Activity启动模式设置为standard,启动后如下图:
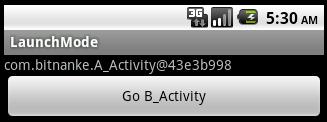
点击button后:
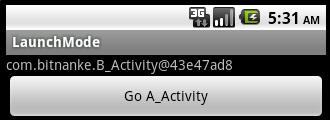
继续点击button:
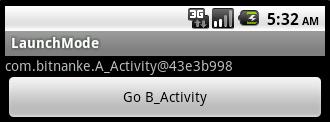
由此可知,singleTask模式的A_Activity在栈中只有一个实例,可以被重复使用
并且,如果收到Intent生成一个新实例,那么用户可以通过回退键回到上一个状态,如果是已经存在的一个activity来处理这个Intent的话,就无法通过回退键回到上一个状态(对singleInstance同样适用) ,比如刚才最后一步如果再按回退键,就会直接退出程序,而不会回到上一步的状态。
四、singleInstance
这个模式下的Activity在一个单独的task栈中,这个栈也只能包含一个Activity的实例,将上面代码稍微改动一下,显示taskId:
A_Activity 中:textView.setText(this.getTaskId()+"");
B_Activity 中:textView.setText(this.getTaskId()+"");
另外将B_Activity 设置为singleInstance模式,A_Activity 设置为standard模式,启动后:
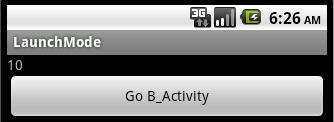
点击button后:
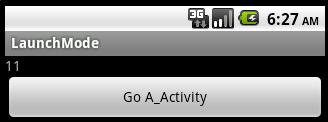
表明启动了新的task
总结四个模式的不同:
1、Intent的目标Activity由哪个task持有
standard与singleTop的Activity所在task,与收到的Intent的发送者所在task相同,除非Intent包括参数FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK,该参数会启动Activity到新的task中;singleTask和singleInstance总是把Activity作为一个task的根元素,它们不会被启动到其他task里
2、是否允许Activity的多个实例
standard与singleTop可以被实例化多次,可以存在不同task中,并且一个task可以包括同一activity的多个实例
singleTask与singleInstance则在同一个task中只能允许Activity的一个实例,并且是task的根元素
3、在同一个task栈中,是否允许其他Activity的实例存在
singleInstance单独在一个task中,其他启动模式允许不同Activity的实例存在
4、是否每次生成新实例接收Intent
standard每次启动都会生成新实例
singleTop的activity如果在task的栈顶的话,则不生成新的activity实例,直接使用该实例,否则,就要生成新的实例
singleInstance在所在栈中是唯一的activity,它每次都会被重用
singleTask如果task栈中有该模式的Activity,就不生成新的activity实例,直接使用该实例,否则,就要生成新的实例
转载:http://blog.csdn.net/leiswpu/article/details/6248528
posted @
2015-04-13 17:56 Terry Zou 阅读(339) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏1. reference:参考某一资源ID。
(1)属性定义:
<declare-styleable name = "名称">
<attr name = "background" format = "reference" />
</declare-styleable>
(2)属性使用:
<ImageView
android:layout_width = "42dip"
android:layout_height = "42dip"
android:background = "@drawable/图片ID"
/>
2. color:颜色值。
(1)属性定义:
<declare-styleable name = "名称">
<attr name = "textColor" format = "color" />
</declare-styleable>
(2)属性使用:
<TextView
android:layout_width = "42dip"
android:layout_height = "42dip"
android:textColor = "#00FF00"
/>
3. boolean:布尔值。
(1)属性定义:
<declare-styleable name = "名称">
<attr name = "focusable" format = "boolean" />
</declare-styleable>
(2)属性使用:
<Button
android:layout_width = "42dip"
android:layout_height = "42dip"
android:focusable = "true"
/>
4. dimension:尺寸值。
(1)属性定义:
<declare-styleable name = "名称">
<attr name = "layout_width" format = "dimension" />
</declare-styleable>
(2)属性使用:
<Button
android:layout_width = "42dip"
android:layout_height = "42dip"
/>
5. float:浮点值。
(1)属性定义:
<declare-styleable name = "AlphaAnimation">
<attr name = "fromAlpha" format = "float" />
<attr name = "toAlpha" format = "float" />
</declare-styleable>
(2)属性使用:
<alpha
android:fromAlpha = "1.0"
android:toAlpha = "0.7"
/>
6. integer:整型值。
(1)属性定义:
<declare-styleable name = "AnimatedRotateDrawable">
<attr name = "visible" />
<attr name = "frameDuration" format="integer" />
<attr name = "framesCount" format="integer" />
<attr name = "pivotX" />
<attr name = "pivotY" />
<attr name = "drawable" />
</declare-styleable>
(2)属性使用:
<animated-rotate
xmlns:android = "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:drawable = "@drawable/图片ID"
android:pivotX = "50%"
android:pivotY = "50%"
android:framesCount = "12"
android:frameDuration = "100"
/>
7. string:字符串。
(1)属性定义:
<declare-styleable name = "MapView">
<attr name = "apiKey" format = "string" />
</declare-styleable>
(2)属性使用:
<com.google.android.maps.MapView
android:layout_width = "fill_parent"
android:layout_height = "fill_parent"
android:apiKey = "0jOkQ80oD1JL9C6HAja99uGXCRiS2CGjKO_bc_g"
/>
8. fraction:百分数。
(1)属性定义:
<declare-styleable name="RotateDrawable">
<attr name = "visible" />
<attr name = "fromDegrees" format = "float" />
<attr name = "toDegrees" format = "float" />
<attr name = "pivotX" format = "fraction" />
<attr name = "pivotY" format = "fraction" />
<attr name = "drawable" />
</declare-styleable>
(2)属性使用:
<rotate
xmlns:android = "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:interpolator = "@anim/动画ID"
android:fromDegrees = "0"
android:toDegrees = "360"
android:pivotX = "200%"
android:pivotY = "300%"
android:duration = "5000"
android:repeatMode = "restart"
android:repeatCount = "infinite"
/>
9. enum:枚举值。
(1)属性定义:
<declare-styleable name="名称">
<attr name="orientation">
<enum name="horizontal" value="0" />
<enum name="vertical" value="1" />
</attr>
</declare-styleable>
(2)属性使用:
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android = "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation = "vertical"
android:layout_width = "fill_parent"
android:layout_height = "fill_parent"
>
</LinearLayout>
10. flag:位或运算。
(1)属性定义:
<declare-styleable name="名称">
<attr name="windowSoftInputMode">
<flag name = "stateUnspecified" value = "0" />
<flag name = "stateUnchanged" value = "1" />
<flag name = "stateHidden" value = "2" />
<flag name = "stateAlwaysHidden" value = "3" />
<flag name = "stateVisible" value = "4" />
<flag name = "stateAlwaysVisible" value = "5" />
<flag name = "adjustUnspecified" value = "0x00" />
<flag name = "adjustResize" value = "0x10" />
<flag name = "adjustPan" value = "0x20" />
<flag name = "adjustNothing" value = "0x30" />
</attr>
</declare-styleable>
(2)属性使用:
<activity
android:name = ".StyleAndThemeActivity"
android:label = "@string/app_name"
android:windowSoftInputMode = "stateUnspecified | stateUnchanged | stateHidden">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name = "android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name = "android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
注意:
属性定义时可以指定多种类型值。
(1)属性定义:
<declare-styleable name = "名称">
<attr name = "background" format = "reference|color" />
</declare-styleable>
(2)属性使用:
<ImageView
android:layout_width = "42dip"
android:layout_height = "42dip"
android:background = "@drawable/图片ID|#00FF00"
/>
posted @
2015-03-23 22:43 Terry Zou 阅读(187) |
评论 (0) |
编辑 收藏