|
|
2010年7月31日
beans.xml   beans<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-2.5.xsd">
<context:annotation-config />
<context:component-scan base-package="cc.rm" />
<bean
class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="locations">
<value>classpath:jdbc.properties</value>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="dataSource" destroy-method="close"
class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName"
value="${jdbc.driverClassName}" />
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" />
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />
</bean>
<!--DataSource -->
<bean id="sf"
class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.annotation.AnnotationSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
<property name="packagesToScan">
<list>
<value>cc.rm.vo</value>
</list>
</property>
<property name="hibernateProperties">
<props>
<prop key="hibernate.dialect">
org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect
</prop>
<prop key="hibernate.show_sql">true</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="hibernateTemplate" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTemplate">
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sf"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="txManager"
class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTransactionManager">
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sf" />
</bean>
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="bussinessService"
expression="execution(public * cc.rm.*.*(..))" />
<aop:advisor pointcut-ref="bussinessService"
advice-ref="txAdvice" />
</aop:config>
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="txManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
</beans> beans<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-2.5.xsd">
<context:annotation-config />
<context:component-scan base-package="cc.rm" />
<bean
class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="locations">
<value>classpath:jdbc.properties</value>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="dataSource" destroy-method="close"
class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName"
value="${jdbc.driverClassName}" />
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" />
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />
</bean>
<!--DataSource -->
<bean id="sf"
class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.annotation.AnnotationSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
<property name="packagesToScan">
<list>
<value>cc.rm.vo</value>
</list>
</property>
<property name="hibernateProperties">
<props>
<prop key="hibernate.dialect">
org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect
</prop>
<prop key="hibernate.show_sql">true</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="hibernateTemplate" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTemplate">
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sf"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="txManager"
class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTransactionManager">
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sf" />
</bean>
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="bussinessService"
expression="execution(public * cc.rm.*.*(..))" />
<aop:advisor pointcut-ref="bussinessService"
advice-ref="txAdvice" />
</aop:config>
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="txManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
</beans>
jdbc.properties
  propertiesjdbc.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/ll
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=1244 propertiesjdbc.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/ll
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=1244
在web.xml里加入
  web.xml<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>WEB-INF/:beans.xml,</param-value>
</context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener> web.xml<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>WEB-INF/:beans.xml,</param-value>
</context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
需要先安装ODBC,才可以使用ODBC连接方式连接数据库 下载地址:mysql-connector-odbc-5.1.8-win32.msi 1 
2 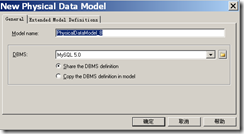
3 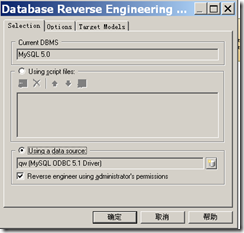
4 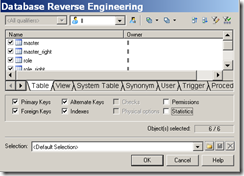
5 
new SchemaExport(new AnnotationConfiguration().configure()).create(false, true);
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='gb2312'?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<!--显示执行的SQL语句-->
<property name="show_sql">true</property>
<!--连接字符串-->
<property name="connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/Test</property>
<!--连接数据库的用户名-->
<property name="connection.username">sa</property>
<!--数据库用户密码-->
<property name="connection.password">sa</property>
<!--数据库驱动-->
<property name="connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<!--JDBC连接池(使用内置的连接池)-->
<property name="connection.pool_size">1</property>
<!--设置Hibernate自动管理上下文的策略-->
<property name="current_session_context_class">thread</property>
<!--选择使用的方言-->
<property name="dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property>
<!--在启动时删除并重新创建数据库-->
<property name="hbm2ddl.auto">create</property>
<mapping resource="events/User.hbm.xml"/>
<mapping resource="events/Student.hbm.xml"/>
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>
一、设计过程包含五个主要步骤。
第 1 步:确定实体和关系
第 2 步:确定所需数据
第 3 步:规范化数据
第 4 步:解析关系
第 5 步:验证设计
二、阅读别人的概念模型图:
不管是从左到右读取还是从右到左读取,下面的规则都会使读取这些图示变得容易:读取 (1) 第一个实体的名称,(2) 第一个实体 旁边的角色,(3) 到第二个实体 的连接的基数,(4) 第二个实体的名称。
三、确定所需数据(实体属性的设计)需要注意的:
确定支持数据时,一定要参考前面确定的活动以了解将如何访问这些数据。
例如,在某些情况下可能需要按雇员的名字列出雇员,而在另一些情况下可能需要按姓氏列出。要满足这两种需要,应创建一个 First Name 属性和一个 Last Name 属性,而不应创建一个既包含名字又包含姓氏的属性。将姓氏和名字分开后,以后可以创建两个索引,分别适用于这两项任务。
请选择一致的名称。使用一致的名称可以使数据库便于维护,并且便于阅读报告和输出窗口。
例如,如果一个属性使用了缩略名称,如 Emp_status,则另一个属性不应使用完整名称,如 Employee_ID。应使名称保持一致,如 Emp_status 和 Emp_ID。
在这个阶段,数据是否与正确的实体相关联并不十分重要。您可以根据自己的判断进行设计。在下一节中,将对设计进行测试,检查您的判断是否正确。
四、规范化是指一系列测试,通过这些测试可以消除冗余的数据,并确保数据与正确的实体或关系相关联。共有五项测试。本节介绍其中前三项测试。这三项测试最重要,因此也最常使用。
五、范式:
数据规范化包括几项测试。数据在通过了第一项测试后,我们认为它满足第一范式;通过了第二项测试后,它满足第二范式;通过了第三项测试后,则满足第三范式。
六、标识符是唯一地标识实体中各行的一组属性,至少由一个属性组成。
七、解析关系:
执行完规范化过程后,设计几乎就完成了。唯一还需要做的事情就是生成与概念数据模型相对应的物理数据模型。这个过程也称作解析关系,因为其中涉及的大量工作就是将概念模型中的关系转换为相应的表和外键关系。
八、概念数据模型可以简化设计过程,因为它将大量细节隐藏起来。例如,多对多关系总会生成一个额外的表和两个外键引用。在概念数据模型中,通常可以用一个连接来标识这类结构。
九、域(用户定义的数据类型)
十、数据库对象的定义构成了数据库模式:您可以将模式看做一个空数据库。(是否可以理解成C#的命名空间或java里的包概念)
十一、
这个插件在JQuery1.5.1版下无法使用。 项目地址:http://dev.iceburg.net/jquery/tableEditor/demo.php html文件:   html<table id="editableTable" border="0" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="0">
<thead>
<tr>
<th name="ID">ID</th>
<th name="first">First Name</th>
<th name="last">Last Name</th>
<th>Phone</th>
<th name="city">City</th>
<th name="email">Email</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><key>233</key> <button class="eventLink">edit</button></td>
<td><input type="text" name="XXXX" val="YYYY"></input></td>
<td>XXX</td>
<td><input type="checkbox" checked name="zzTop"></input></td>
<td><input type="checkbox" name="yyy"></input></td>
<td><select name="yyy"><option>XXX</option><option SELECTED>YYY</option></select></td>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td><key>1</key> <button class="eventLink">edit</button></td>
<td>Brice</td>
<td>Burgess</td>
<td>(800)768-5283</td>
<td>Milwaukee</td>
<td>b@b.com</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><key>2</key> <button class="eventLink">edit</button></td>
<td>Christian</td>
<td>Bach</td>
<td>(800)768-6288</td>
<td>Chicago</td>
<td>c@c.com</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><key>3</key> <button class="eventLink">edit</button></td>
<td>Abe</td>
<td>Lincoln</td>
<td>(800)223-2331</td>
<td>Washington D.C.</td>
<td>l@l.com</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><key>8</key> <button class="eventLink">edit</button></td>
<td>Sam Lightning</td>
<td>Hopkings</td>
<td>(800)728-1221</td>
<td>Houston</td>
<td>s@s.com</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><key>15</key> <button class="eventLink">edit</button></td>
<td>Rudyard</td>
<td>Kipling</td>
<td>(512)121-1280</td>
<td>London</td>
<td>r@r.com</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table> html<table id="editableTable" border="0" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="0">
<thead>
<tr>
<th name="ID">ID</th>
<th name="first">First Name</th>
<th name="last">Last Name</th>
<th>Phone</th>
<th name="city">City</th>
<th name="email">Email</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><key>233</key> <button class="eventLink">edit</button></td>
<td><input type="text" name="XXXX" val="YYYY"></input></td>
<td>XXX</td>
<td><input type="checkbox" checked name="zzTop"></input></td>
<td><input type="checkbox" name="yyy"></input></td>
<td><select name="yyy"><option>XXX</option><option SELECTED>YYY</option></select></td>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td><key>1</key> <button class="eventLink">edit</button></td>
<td>Brice</td>
<td>Burgess</td>
<td>(800)768-5283</td>
<td>Milwaukee</td>
<td>b@b.com</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><key>2</key> <button class="eventLink">edit</button></td>
<td>Christian</td>
<td>Bach</td>
<td>(800)768-6288</td>
<td>Chicago</td>
<td>c@c.com</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><key>3</key> <button class="eventLink">edit</button></td>
<td>Abe</td>
<td>Lincoln</td>
<td>(800)223-2331</td>
<td>Washington D.C.</td>
<td>l@l.com</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><key>8</key> <button class="eventLink">edit</button></td>
<td>Sam Lightning</td>
<td>Hopkings</td>
<td>(800)728-1221</td>
<td>Houston</td>
<td>s@s.com</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><key>15</key> <button class="eventLink">edit</button></td>
<td>Rudyard</td>
<td>Kipling</td>
<td>(512)121-1280</td>
<td>London</td>
<td>r@r.com</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
js文件
  js<script type="text/javascript">
$().ready(function() {
$("#editableTable").tableSorter({
sortClassAsc: 'headerSortUp', // class name for ascending sorting action to header
sortClassDesc: 'headerSortDown', // class name for descending sorting action to header
headerClass: 'header', // class name for headers (th's)
disableHeader: 'ID' // DISABLE Sorting on ID
}).tableEditor({
EDIT_HTML: 'edit',
SAVE_HTML: 'save',
EVENT_LINK_SELECTOR: 'button.eventLink',
FUNC_UPDATE: 'updateTable'
});
document.counter = 0;
});
function updateTable(o) {
document.counter++;
if ((document.counter%2) == 0) {
// restore row
alert('Update failed. Row restore.');
$.tableEditor.lib.restoreRow(o.row,o.original);
}
else
alert('Update Success');
return true;
}
</script> js<script type="text/javascript">
$().ready(function() {
$("#editableTable").tableSorter({
sortClassAsc: 'headerSortUp', // class name for ascending sorting action to header
sortClassDesc: 'headerSortDown', // class name for descending sorting action to header
headerClass: 'header', // class name for headers (th's)
disableHeader: 'ID' // DISABLE Sorting on ID
}).tableEditor({
EDIT_HTML: 'edit',
SAVE_HTML: 'save',
EVENT_LINK_SELECTOR: 'button.eventLink',
FUNC_UPDATE: 'updateTable'
});
document.counter = 0;
});
function updateTable(o) {
document.counter++;
if ((document.counter%2) == 0) {
// restore row
alert('Update failed. Row restore.');
$.tableEditor.lib.restoreRow(o.row,o.original);
}
else
alert('Update Success');
return true;
}
</script>
从DLOG4J读到的Request的工具类:   java/*
* RequestUtils.java
*
* This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
* it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
* the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or
* (at your option) any later version.
*
* This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
* GNU Library General Public License for more details.
*
* You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
* along with this program; if not, write to the Free Software
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place - Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307, USA.
*
* Author: Winter Lau (javayou@gmail.com)
* http://dlog4j.sourceforge.net
*/
package com.liusoft.dlog4j.util;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.text.MessageFormat;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.servlet.http.Cookie;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;
import com.liusoft.dlog4j.Globals;
/**
* 用于Request的工具类
* @author Winter Lau
*/
public class RequestUtils extends org.apache.struts.util.RequestUtils{
final static Log log = LogFactory.getLog(RequestUtils.class);
private static Properties header_map;
private static String default_mobile;
static{
InputStream in = RequestUtils.class.getResourceAsStream("/com/liusoft/dlog4j/util/mobile_match.properties");
header_map = new Properties();
try{
header_map.load(in);
default_mobile = header_map.getProperty("empty");
}catch(IOException e){
log.error("加载手机号码匹配策略文件/mobile_match.conf失败",e);
}
}
public static boolean isMultipart(HttpServletRequest req) {
return ((req.getContentType() != null) && (req.getContentType()
.toLowerCase().startsWith("multipart")));
}
/**
* 获取FCKUpload过程中生成的会话ID
* @return
*/
public static String getDlogSessionId(HttpServletRequest req){
//优先从Cookie中获取ssn_id值
String ssn_id = null;
Cookie cok = RequestUtils.getCookie(req, Globals.SESSION_ID_KEY_IN_COOKIE);
if(cok != null){
ssn_id = cok.getValue();
}
if(StringUtils.isEmpty(ssn_id)){
//如果Cookie得不到则从服务器的会话中读取
HttpSession ssn = req.getSession(false);
if (ssn != null)
ssn_id = ssn.getId();
}
return ssn_id;
}
/**
* 清除FCKUpload过程中生成的Cookie
* @param req
* @param res
*/
public static void clearDlogSessionId(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse res){
Cookie cok = RequestUtils.getCookie(req, Globals.SESSION_ID_KEY_IN_COOKIE);
if(cok != null){
cok.setMaxAge(0);
res.addCookie(cok);
}
}
/**
* 获取COOKIE
*
* @param name
*/
public static Cookie getCookie(HttpServletRequest request, String name) {
Cookie[] cookies = request.getCookies();
if(cookies == null)
return null;
for (int i = 0; i < cookies.length; i++) {
if (name.equals(cookies[i].getName())) {
return cookies[i];
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* 设置COOKIE
*
* @param name
* @param value
* @param maxAge
*/
public static void setCookie(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, String name,
String value, int maxAge) {
Cookie cookie = new Cookie(name, value);
cookie.setMaxAge(maxAge);
String serverName = request.getServerName();
String domain = getDomainOfServerName(serverName);
if(domain!=null && domain.indexOf('.')!=-1){
cookie.setDomain('.' + domain);
}
cookie.setPath("/");
response.addCookie(cookie);
}
/**
* 获取用户访问URL中的根域名
* 例如: www.dlog.cn -> dlog.cn
* @param req
* @return
*/
public static String getDomainOfServerName(String host){
if(StringUtils.isIPAddr(host))
return null;
String[] names = StringUtils.split(host, '.');
int len = names.length;
if(len>=2)
return names[len-2]+'.'+names[len-1];
return host;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
String host = "127.0.0.1";
System.out.println("DOMAIN: " + getDomainOfServerName(host));
host = "dlog.cn";
System.out.println("DOMAIN: " + getDomainOfServerName(host));
host = "abc.mail.dlog.cn";
System.out.println("DOMAIN: " + getDomainOfServerName(host));
}
/**
* 从URL地址中解析出URL前缀,例如
* http://wap.mo168.com:8081/index.jsp -> http://wap.mo168.com:8081
* @param req
* @return
*/
public static String getUrlPrefix(HttpServletRequest req){
StringBuffer url = new StringBuffer(req.getScheme());
url.append("://");
url.append(req.getServerName());
int port = req.getServerPort();
if(port!=80){
url.append(":");
url.append(port);
}
return url.toString();
}
/**
* 获取访问的URL全路径
* @param req
* @return
*/
public static String getRequestURL(HttpServletRequest req){
StringBuffer url = new StringBuffer(req.getRequestURI());
String param = req.getQueryString();
if(param!=null){
url.append('?');
url.append(param);
}
String path = url.toString();
return path.substring(req.getContextPath().length());
}
/**
* 打印所有的头信息
* @param out
* @param req
*/
public static void dumpHeaders(PrintStream out, HttpServletRequest req){
Enumeration names = req.getHeaderNames();
while(names.hasMoreElements()){
String name = (String)names.nextElement();
out.println(name+"="+req.getHeader(name));
}
}
/**
* 从请求中解析手机号码
* @param req
* @return
*/
public static String getRequestMobile(HttpServletRequest req){
String mobile = default_mobile;
Iterator keys = header_map.keySet().iterator();
while(keys.hasNext()){
String header = (String)keys.next();
String value = getHeader(req,header);
if(value!=null){
String pattern = (String)header_map.get(header);
MessageFormat mf = new MessageFormat(pattern);
try{
Object[] vs = mf.parse(value);
mobile = (String)vs[0];
if(mobile.startsWith("86"))
mobile = mobile.substring(2);
break;
}catch(Exception e){
log.warn("解析header失败",e);
dumpHeaders(req, System.err);
continue;
}
}
}
return mobile;
}
/**
* 获取header信息,名字大小写无关
* @param req
* @param name
* @return
*/
public static String getHeader(HttpServletRequest req, String name){
String value = req.getHeader(name);
if(value!=null)
return value;
Enumeration names = req.getHeaderNames();
while(names.hasMoreElements()){
String n = (String)names.nextElement();
if(n.equalsIgnoreCase(name)){
return req.getHeader(n);
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* 打印所有头信息
* @param req
* @param out
*/
public static void dumpHeaders(HttpServletRequest req, PrintStream out){
Enumeration hds = req.getHeaderNames();
out.println("=============== HEADERS ===============");
while(hds.hasMoreElements()){
String name = (String)hds.nextElement();
out.println(name+"="+req.getHeader(name));
}
}
/**
* 判断手机是否支持某种类型的格式
* @param req
* @param contentType
* @return
*/
public static boolean support(HttpServletRequest req, String contentType){
String accept = getHeader(req, "accept");
if(accept!=null){
accept = accept.toLowerCase();
return accept.indexOf(contentType.toLowerCase())!=-1;
}
return false;
}
/**
* 判断浏览器是否与Mozilla兼容
* @param req
* @return
*/
public static boolean isMozillaCompatible(HttpServletRequest req){
String user_agent = req.getHeader("user-agent");
return user_agent==null || user_agent.indexOf("Mozilla")!=-1;
}
/**
* 获取浏览器提交的整形参数
* @param param
* @param defaultValue
* @return
*/
public static int getParam(HttpServletRequest req, String param, int defaultValue){
try{
String value = req.getParameter(param);
int idx = value.indexOf('#');
if(idx!=-1)
value = value.substring(0,idx);
return Integer.parseInt(value);
}catch(Exception e){}
return defaultValue;
}
/**
* 获取浏览器提交的字符串参数
* @param param
* @param defaultValue
* @return
*/
public static String getParam(HttpServletRequest req, String param, String defaultValue){
String value = req.getParameter(param);
return (StringUtils.isEmpty(value))?defaultValue:value;
}
} java/*
* RequestUtils.java
*
* This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
* it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
* the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or
* (at your option) any later version.
*
* This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
* GNU Library General Public License for more details.
*
* You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
* along with this program; if not, write to the Free Software
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place - Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307, USA.
*
* Author: Winter Lau (javayou@gmail.com)
* http://dlog4j.sourceforge.net
*/
package com.liusoft.dlog4j.util;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.text.MessageFormat;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.servlet.http.Cookie;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;
import com.liusoft.dlog4j.Globals;
/**
* 用于Request的工具类
* @author Winter Lau
*/
public class RequestUtils extends org.apache.struts.util.RequestUtils{
final static Log log = LogFactory.getLog(RequestUtils.class);
private static Properties header_map;
private static String default_mobile;
static{
InputStream in = RequestUtils.class.getResourceAsStream("/com/liusoft/dlog4j/util/mobile_match.properties");
header_map = new Properties();
try{
header_map.load(in);
default_mobile = header_map.getProperty("empty");
}catch(IOException e){
log.error("加载手机号码匹配策略文件/mobile_match.conf失败",e);
}
}
public static boolean isMultipart(HttpServletRequest req) {
return ((req.getContentType() != null) && (req.getContentType()
.toLowerCase().startsWith("multipart")));
}
/**
* 获取FCKUpload过程中生成的会话ID
* @return
*/
public static String getDlogSessionId(HttpServletRequest req){
//优先从Cookie中获取ssn_id值
String ssn_id = null;
Cookie cok = RequestUtils.getCookie(req, Globals.SESSION_ID_KEY_IN_COOKIE);
if(cok != null){
ssn_id = cok.getValue();
}
if(StringUtils.isEmpty(ssn_id)){
//如果Cookie得不到则从服务器的会话中读取
HttpSession ssn = req.getSession(false);
if (ssn != null)
ssn_id = ssn.getId();
}
return ssn_id;
}
/**
* 清除FCKUpload过程中生成的Cookie
* @param req
* @param res
*/
public static void clearDlogSessionId(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse res){
Cookie cok = RequestUtils.getCookie(req, Globals.SESSION_ID_KEY_IN_COOKIE);
if(cok != null){
cok.setMaxAge(0);
res.addCookie(cok);
}
}
/**
* 获取COOKIE
*
* @param name
*/
public static Cookie getCookie(HttpServletRequest request, String name) {
Cookie[] cookies = request.getCookies();
if(cookies == null)
return null;
for (int i = 0; i < cookies.length; i++) {
if (name.equals(cookies[i].getName())) {
return cookies[i];
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* 设置COOKIE
*
* @param name
* @param value
* @param maxAge
*/
public static void setCookie(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, String name,
String value, int maxAge) {
Cookie cookie = new Cookie(name, value);
cookie.setMaxAge(maxAge);
String serverName = request.getServerName();
String domain = getDomainOfServerName(serverName);
if(domain!=null && domain.indexOf('.')!=-1){
cookie.setDomain('.' + domain);
}
cookie.setPath("/");
response.addCookie(cookie);
}
/**
* 获取用户访问URL中的根域名
* 例如: www.dlog.cn -> dlog.cn
* @param req
* @return
*/
public static String getDomainOfServerName(String host){
if(StringUtils.isIPAddr(host))
return null;
String[] names = StringUtils.split(host, '.');
int len = names.length;
if(len>=2)
return names[len-2]+'.'+names[len-1];
return host;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
String host = "127.0.0.1";
System.out.println("DOMAIN: " + getDomainOfServerName(host));
host = "dlog.cn";
System.out.println("DOMAIN: " + getDomainOfServerName(host));
host = "abc.mail.dlog.cn";
System.out.println("DOMAIN: " + getDomainOfServerName(host));
}
/**
* 从URL地址中解析出URL前缀,例如
* http://wap.mo168.com:8081/index.jsp -> http://wap.mo168.com:8081
* @param req
* @return
*/
public static String getUrlPrefix(HttpServletRequest req){
StringBuffer url = new StringBuffer(req.getScheme());
url.append("://");
url.append(req.getServerName());
int port = req.getServerPort();
if(port!=80){
url.append(":");
url.append(port);
}
return url.toString();
}
/**
* 获取访问的URL全路径
* @param req
* @return
*/
public static String getRequestURL(HttpServletRequest req){
StringBuffer url = new StringBuffer(req.getRequestURI());
String param = req.getQueryString();
if(param!=null){
url.append('?');
url.append(param);
}
String path = url.toString();
return path.substring(req.getContextPath().length());
}
/**
* 打印所有的头信息
* @param out
* @param req
*/
public static void dumpHeaders(PrintStream out, HttpServletRequest req){
Enumeration names = req.getHeaderNames();
while(names.hasMoreElements()){
String name = (String)names.nextElement();
out.println(name+"="+req.getHeader(name));
}
}
/**
* 从请求中解析手机号码
* @param req
* @return
*/
public static String getRequestMobile(HttpServletRequest req){
String mobile = default_mobile;
Iterator keys = header_map.keySet().iterator();
while(keys.hasNext()){
String header = (String)keys.next();
String value = getHeader(req,header);
if(value!=null){
String pattern = (String)header_map.get(header);
MessageFormat mf = new MessageFormat(pattern);
try{
Object[] vs = mf.parse(value);
mobile = (String)vs[0];
if(mobile.startsWith("86"))
mobile = mobile.substring(2);
break;
}catch(Exception e){
log.warn("解析header失败",e);
dumpHeaders(req, System.err);
continue;
}
}
}
return mobile;
}
/**
* 获取header信息,名字大小写无关
* @param req
* @param name
* @return
*/
public static String getHeader(HttpServletRequest req, String name){
String value = req.getHeader(name);
if(value!=null)
return value;
Enumeration names = req.getHeaderNames();
while(names.hasMoreElements()){
String n = (String)names.nextElement();
if(n.equalsIgnoreCase(name)){
return req.getHeader(n);
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* 打印所有头信息
* @param req
* @param out
*/
public static void dumpHeaders(HttpServletRequest req, PrintStream out){
Enumeration hds = req.getHeaderNames();
out.println("=============== HEADERS ===============");
while(hds.hasMoreElements()){
String name = (String)hds.nextElement();
out.println(name+"="+req.getHeader(name));
}
}
/**
* 判断手机是否支持某种类型的格式
* @param req
* @param contentType
* @return
*/
public static boolean support(HttpServletRequest req, String contentType){
String accept = getHeader(req, "accept");
if(accept!=null){
accept = accept.toLowerCase();
return accept.indexOf(contentType.toLowerCase())!=-1;
}
return false;
}
/**
* 判断浏览器是否与Mozilla兼容
* @param req
* @return
*/
public static boolean isMozillaCompatible(HttpServletRequest req){
String user_agent = req.getHeader("user-agent");
return user_agent==null || user_agent.indexOf("Mozilla")!=-1;
}
/**
* 获取浏览器提交的整形参数
* @param param
* @param defaultValue
* @return
*/
public static int getParam(HttpServletRequest req, String param, int defaultValue){
try{
String value = req.getParameter(param);
int idx = value.indexOf('#');
if(idx!=-1)
value = value.substring(0,idx);
return Integer.parseInt(value);
}catch(Exception e){}
return defaultValue;
}
/**
* 获取浏览器提交的字符串参数
* @param param
* @param defaultValue
* @return
*/
public static String getParam(HttpServletRequest req, String param, String defaultValue){
String value = req.getParameter(param);
return (StringUtils.isEmpty(value))?defaultValue:value;
}
}
  java/*
* SiteAction.java
*
* This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
* it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
* the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or
* (at your option) any later version.
*
* This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
* GNU Library General Public License for more details.
*
* You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
* along with this program; if not, write to the Free Software
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place - Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307, USA.
*
* Author: Winter Lau
* http://dlog4j.sourceforge.net
*/
package com.liusoft.dlog4j;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import org.apache.commons.lang.StringUtils;
/**
* DLOG在安全方面的一些处理方法
* 敏感词汇表:/WEB-INF/conf/illegal_glossary.dat
*
* @author Winter Lau
*/
public class DLOGSecurityManager {
/**
* 初始化
* @param sc
* @throws IOException
*
* @see com.liusoft.dlog4j.servlet.DLOG_ActionServlet#init()
*/
public static void init(ServletContext sc) throws IOException {
IllegalGlossary.init(sc);
}
public static void destroy(){
IllegalGlossary.destroy();
}
/**
* 敏感字汇
* @author Winter Lau
*/
public static class IllegalGlossary {
private final static String file_glossary = "/WEB-INF/conf/illegal_glossary.dat";
private static List glossary = null;
public static void init(ServletContext sc) throws IOException {
glossary = new ArrayList(1000);
if(sc!=null)
loadIllegalGlossary(sc);
}
public static void destroy(){
if(glossary!=null)
glossary.clear();
}
/**
* 加载敏感词汇表
* @param sc
* @throws IOException
*/
private synchronized static void loadIllegalGlossary(ServletContext sc) throws IOException {
InputStream in = sc.getResourceAsStream(file_glossary);
BufferedReader reader = null;
try{
reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(in));
do{
String line = reader.readLine();
if(line==null)
break;
glossary.add(line.trim());
}while(true);
}finally{
in.close();
}
}
/**
* 自动将敏感词汇用XXX替换
*
* @param content
* @return
*/
public static String autoGlossaryFiltrate(String content) {
if(StringUtils.isEmpty(content))
return content;
for (int i = 0; i < glossary.size(); i++) {
String word = (String)glossary.get(i);
content = StringUtils.replace(content, word, StringUtils
.repeat("X", word.length()));
}
return content;
}
/**
* 判断是否存在非法内容
* @param content
* @return
*/
public static boolean existIllegalWord(String content){
if(StringUtils.isEmpty(content))
return false;
for (int i = 0; i < glossary.size(); i++) {
String word = (String) glossary.get(i);
if(content.indexOf(word)>=0)
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* 删除内容中存在的关键字
* @param content
* @return
*/
public static String deleteIllegalWord(String content){
if(StringUtils.isEmpty(content))
return content;
for (int i = 0; i < glossary.size(); i++) {
String word = (String) glossary.get(i);
content = StringUtils.remove(content, word);
}
return content;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
init(null);
String text = "中华人民共和国国家主席毛泽东,我们叫他毛主席";
System.out.println(IllegalGlossary.autoGlossaryFiltrate(text));
}
} java/*
* SiteAction.java
*
* This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
* it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
* the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or
* (at your option) any later version.
*
* This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
* GNU Library General Public License for more details.
*
* You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
* along with this program; if not, write to the Free Software
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place - Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307, USA.
*
* Author: Winter Lau
* http://dlog4j.sourceforge.net
*/
package com.liusoft.dlog4j;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import org.apache.commons.lang.StringUtils;
/**
* DLOG在安全方面的一些处理方法
* 敏感词汇表:/WEB-INF/conf/illegal_glossary.dat
*
* @author Winter Lau
*/
public class DLOGSecurityManager {
/**
* 初始化
* @param sc
* @throws IOException
*
* @see com.liusoft.dlog4j.servlet.DLOG_ActionServlet#init()
*/
public static void init(ServletContext sc) throws IOException {
IllegalGlossary.init(sc);
}
public static void destroy(){
IllegalGlossary.destroy();
}
/**
* 敏感字汇
* @author Winter Lau
*/
public static class IllegalGlossary {
private final static String file_glossary = "/WEB-INF/conf/illegal_glossary.dat";
private static List glossary = null;
public static void init(ServletContext sc) throws IOException {
glossary = new ArrayList(1000);
if(sc!=null)
loadIllegalGlossary(sc);
}
public static void destroy(){
if(glossary!=null)
glossary.clear();
}
/**
* 加载敏感词汇表
* @param sc
* @throws IOException
*/
private synchronized static void loadIllegalGlossary(ServletContext sc) throws IOException {
InputStream in = sc.getResourceAsStream(file_glossary);
BufferedReader reader = null;
try{
reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(in));
do{
String line = reader.readLine();
if(line==null)
break;
glossary.add(line.trim());
}while(true);
}finally{
in.close();
}
}
/**
* 自动将敏感词汇用XXX替换
*
* @param content
* @return
*/
public static String autoGlossaryFiltrate(String content) {
if(StringUtils.isEmpty(content))
return content;
for (int i = 0; i < glossary.size(); i++) {
String word = (String)glossary.get(i);
content = StringUtils.replace(content, word, StringUtils
.repeat("X", word.length()));
}
return content;
}
/**
* 判断是否存在非法内容
* @param content
* @return
*/
public static boolean existIllegalWord(String content){
if(StringUtils.isEmpty(content))
return false;
for (int i = 0; i < glossary.size(); i++) {
String word = (String) glossary.get(i);
if(content.indexOf(word)>=0)
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* 删除内容中存在的关键字
* @param content
* @return
*/
public static String deleteIllegalWord(String content){
if(StringUtils.isEmpty(content))
return content;
for (int i = 0; i < glossary.size(); i++) {
String word = (String) glossary.get(i);
content = StringUtils.remove(content, word);
}
return content;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
init(null);
String text = "中华人民共和国国家主席毛泽东,我们叫他毛主席";
System.out.println(IllegalGlossary.autoGlossaryFiltrate(text));
}
}
这个类,是从DLOG4J上学到的。
  sqlDROP DATABASE IF EXISTS `local` ;
CREATE DATABASE `local`;
use `local` ;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS actionmanager;
CREATE TABLE actionmanager(
actionid INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY ,
actionName VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL ,
action VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
createDate DATE,
viewmode INT DEFAULT 0
#index inx(`action`)
)type=InnoDB;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS actioncolumn ;
CREATE TABLE actioncolumn(
actioncolumnid INT AUTO_INCREMENT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY ,
actioncolumnname VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL
)type=InnoDB;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS groupmanager;
CREATE TABLE groupmanager(
groupid INT AUTO_INCREMENT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY ,
groupname VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
groupinfo VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT NULL,
masterid INT NOT NULL, #who created this group
mastername VARCHAR(255),
createdate DATE
)type=InnoDB;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS master;
CREATE TABLE master(
id INT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL ,
password VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL ,
sex VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL ,
position VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
masterid INT , #whoe created this master
mastername VARCHAR(255),
createdate DATE
)type=InnoDB;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS actiongroup ;
CREATE TABLE actiongroup(
id INT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
`action` VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
groupid INT NOT NULL ,
masterid int NOT NULL,
mastername VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL ,
createdate DATE,
index inx_ag(`action`)
)type=InnoDB;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS mastergroup ;
CREATE TABLE mastergroup(
id INT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
masterid INT NOT NULL ,
groupid INT NOT NULL ,
masterid2 INT NOT NULL , # who created or modified this mastergroup
creatDate DATE
)type=InnoDB ;
##############action link group ######################
CREATE INDEX idx_actionmanager_action ON actionmanager(`action`);
CREATE INDEX idx_groupmanager_groupid ON groupmanager(`groupid`);
ALTER TABLE actiongroup
ADD CONSTRAINT fk_action
FOREIGN KEY (action) REFERENCES actionmanager(`action`)
ON DELETE CASCADE ON UPDATE CASCADE;
ALTER TABLE actiongroup
ADD CONSTRAINT fk_groupid
FOREIGN KEY (groupid) REFERENCES groupmanager(`groupid`)
ON DELETE CASCADE ON UPDATE CASCADE;
##############action link master######################
CREATE INDEX idx_master_id ON master(`id`);
ALTER TABLE mastergroup
ADD CONSTRAINT fk_masterg_mid
FOREIGN KEY (masterid) REFERENCES master(`id`)
ON DELETE CASCADE ON UPDATE CASCADE;
ALTER TABLE mastergroup
ADD CONSTRAINT fk_masterg_gid
FOREIGN KEY (groupid) REFERENCES groupmanager(`groupid`)
ON DELETE CASCADE ON UPDATE CASCADE; sqlDROP DATABASE IF EXISTS `local` ;
CREATE DATABASE `local`;
use `local` ;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS actionmanager;
CREATE TABLE actionmanager(
actionid INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY ,
actionName VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL ,
action VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
createDate DATE,
viewmode INT DEFAULT 0
#index inx(`action`)
)type=InnoDB;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS actioncolumn ;
CREATE TABLE actioncolumn(
actioncolumnid INT AUTO_INCREMENT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY ,
actioncolumnname VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL
)type=InnoDB;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS groupmanager;
CREATE TABLE groupmanager(
groupid INT AUTO_INCREMENT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY ,
groupname VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
groupinfo VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT NULL,
masterid INT NOT NULL, #who created this group
mastername VARCHAR(255),
createdate DATE
)type=InnoDB;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS master;
CREATE TABLE master(
id INT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL ,
password VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL ,
sex VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL ,
position VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
masterid INT , #whoe created this master
mastername VARCHAR(255),
createdate DATE
)type=InnoDB;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS actiongroup ;
CREATE TABLE actiongroup(
id INT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
`action` VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
groupid INT NOT NULL ,
masterid int NOT NULL,
mastername VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL ,
createdate DATE,
index inx_ag(`action`)
)type=InnoDB;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS mastergroup ;
CREATE TABLE mastergroup(
id INT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
masterid INT NOT NULL ,
groupid INT NOT NULL ,
masterid2 INT NOT NULL , # who created or modified this mastergroup
creatDate DATE
)type=InnoDB ;
##############action link group ######################
CREATE INDEX idx_actionmanager_action ON actionmanager(`action`);
CREATE INDEX idx_groupmanager_groupid ON groupmanager(`groupid`);
ALTER TABLE actiongroup
ADD CONSTRAINT fk_action
FOREIGN KEY (action) REFERENCES actionmanager(`action`)
ON DELETE CASCADE ON UPDATE CASCADE;
ALTER TABLE actiongroup
ADD CONSTRAINT fk_groupid
FOREIGN KEY (groupid) REFERENCES groupmanager(`groupid`)
ON DELETE CASCADE ON UPDATE CASCADE;
##############action link master######################
CREATE INDEX idx_master_id ON master(`id`);
ALTER TABLE mastergroup
ADD CONSTRAINT fk_masterg_mid
FOREIGN KEY (masterid) REFERENCES master(`id`)
ON DELETE CASCADE ON UPDATE CASCADE;
ALTER TABLE mastergroup
ADD CONSTRAINT fk_masterg_gid
FOREIGN KEY (groupid) REFERENCES groupmanager(`groupid`)
ON DELETE CASCADE ON UPDATE CASCADE;
1 --创建表
2 if exists(select * from sysobjects where name='user' and type='U') drop table [user] ;
3 create table [user](
4 id int identity(1,1) , --自增字段
5 name varchar(50) ,
6 pwd varchar(50) ,
7 constraint pk_user_id primary key(id) --主键
8 --constraint pk_user_id primary key(id,[name])
9 );
10
11 -- 变量的声明,sql里面声明变量时必须在变量前加@符号
12 DECLARE @I INT
13
14 -- 变量的赋值,变量赋值时变量前必须加set
15 SET @I = 30
16
17 -- 声明多个变量
18 DECLARE @s varchar(10),@a INT
19
20 -- Sql 里if语句
21 IF 条件 BEGIN
22 执行语句
23 END
24 ELSE BEGIN
25 执行语句
26 END
27
28 DECLARE @d INT
29 set @d = 1
30
31 IF @d = 1 BEGIN
32
33 -- 打印
34 PRINT '正确'
35 END
36 ELSE BEGIN
37 PRINT '错误'
38 END
39
40
41 -- Sql 里的多条件选择语句.
42 DECLARE @iRet INT, @PKDisp VARCHAR(20)
43 SET @iRet = 1
44 Select @iRet =
45 CASE
46 WHEN @PKDisp = '一' THEN 1
47 WHEN @PKDisp = '二' THEN 2
48 WHEN @PKDisp = '三' THEN 3
49 WHEN @PKDisp = '四' THEN 4
50 WHEN @PKDisp = '五' THEN 5
51 ELSE 100
52 END
53
54 -- 循环语句
55 WHILE 条件 BEGIN
56 执行语句
57 END
58
59 DECLARE @i INT
60 SET @i = 1
61 WHILE @i<1000000 BEGIN
62 set @i=@i+1
63 END
64 -- 打印
65 PRINT @i
66
67
68 -- TRUNCATE 删除表中的所有行,而不记录单个行删除操作,不能带条件
69
70 /*
71 TRUNCATE TABLE 在功能上与不带 Where 子句的 Delete 语句相同:二者均删除表中的全部行
72
73 。但 TRUNCATE TABLE 比 Delete 速度快,且使用的系统和事务日志资源少。
74 Delete 语句每次删除一行,并在事务日志中为所删除的每行记录一项。TRUNCATE TABLE 通过
75
76 释放存储表数据所用的数据页来删除数据,并且只在事务日志中记录页的释放。
77 TRUNCATE TABLE 删除表中的所有行,但表结构及其列、约束、索引等保持不变。新行标识所用
78
79 的计数值重置为该列的种子。如果想保留标识计数值,请改用 Delete。如果要删除表定义及其数据,请
80
81 使用 Drop TABLE 语句。
82 对于由 FOREIGN KEY 约束引用的表,不能使用 TRUNCATE TABLE,而应使用不带 Where 子句的
83
84 Delete 语句。由于 TRUNCATE TABLE 不记录在日志中,所以它不能激活触发器。
85 TRUNCATE TABLE 不能用于参与了索引视图的表。
86 示例
87 下例删除 authors 表中的所有数据。*/
88
89 TRUNCATE TABLE authors
90
91
92 -- Select INTO 从一个查询的计算结果中创建一个新表。 数据并不返回给客户端,这一点和普通的
93 -- Select 不同。 新表的字段具有和 Select 的输出字段相关联(相同)的名字和数据类型。
94
95 select * into NewTable
96 from Uname
97
98
99 -- Insert INTO Select
100 -- 表ABC必须存在
101 -- 把表Uname里面的字段Username复制到表ABC
102 Insert INTO ABC Select Username FROM Uname
103
104 -- 创建临时表
105 Create TABLE #temp(
106 UID int identity(1, 1) PRIMARY KEY,
107 UserName varchar(16),
108 Pwd varchar(50),
109 Age smallint,
110 Sex varchar(6)
111 )
112 -- 打开临时表
113 Select * from #temp
114
115 -- 存储过程
116 -- 要创建存储过程的数据库
117 Use Test
118 -- 判断要创建的存储过程名是否存在
119 if Exists(Select name From sysobjects Where name='csp_AddInfo' And
120
121 type='P')
122 -- 删除存储过程
123 Drop Procedure dbo.csp_AddInfo
124 Go
125
126
127 -- 创建存储过程
128 Create Proc dbo.csp_AddInfo
129 -- 存储过程参数
130 @UserName varchar(16),
131 @Pwd varchar(50),
132 @Age smallint,
133 @Sex varchar(6)
134 AS
135 -- 存储过程语句体
136 insert into Uname (UserName,Pwd,Age,Sex)
137 values (@UserName,@Pwd,@Age,@Sex)
138 RETURN
139 -- 执行
140 GO
141
142 -- 执行存储过程
143 EXEC csp_AddInfo 'Junn.A','123456',20,'男';
144 修改自:http://blog.csdn.net/mx1029/archive/2007/07/06/1680910.aspx
1、 ServletFileUpload.isMultipartContent(request) 检测request中是否包含有multipart内容 2、如果有,生成DiskFileItemFactory工厂将进行相关的设置 DiskFileItemFactory factory = new DiskFileItemFactory();
// maximum size that will be stored in memory
factory.setSizeThreshold(maxMemSize);
// Location to save data that is larger than maxMemSize.
factory.setRepository(new File("d:/")); 3、生成上传ServletFileUpload类,并将DiskFileFactory工厂传给它,并对ServletFileUpload进行配置 // Create a new file upload handler
ServletFileUpload upload = new ServletFileUpload(factory);
// maximum file size to be uploaded.
upload.setSizeMax(maxFileSize); 4、从request得到上传的文件列表 // Parse the request to get file items.
List fileItems = upload.parseRequest(request); // Process the uploaded file items
Iterator i = fileItems.iterator(); 5、处理文件:写入或者其他操作 while (i.hasNext()) {
FileItem fi = (FileItem) i.next();
if (!fi.isFormField()) {
// Get the uploaded file parameters
String fieldName = fi.getFieldName();
String fileName = fi.getName();
String contentType = fi.getContentType();
boolean isInMemory = fi.isInMemory();
long sizeInBytes = fi.getSize();
// Write the file
if (fileName.lastIndexOf("\\") >= 0) {
file = new File(
filePath
+ fileName.substring(fileName
.lastIndexOf("\\")));
} else {
file = new File(
filePath
+ fileName.substring(fileName
.lastIndexOf("\\") + 1));
}
fi.write(file);
out.println("Uploaded Filename: " + fileName + "<br>");
}
} } 说明: FileItem接口是对用户上传文件的封装 DiskFileItemFactory实现了FileItemFactory接口,主要方法有public FileItem createItem(String fieldName, String contentType, boolean isFormField, String fileName) ServletFileUpload从FileUpload继承,而FileUpload又从FileUploadBase继承,功能:分析传入的request对象、得到文件列表FileItemIterator……
简明步骤 1、下载所需包:commons-FileUpload http://commons.apache.org/fileupload/ 依赖commons-IO包 commons-IO http://commons.apache.org/io/ 2、前端: 3、书写Servlet 4、web.xml中配置上传文件存放地址 5、web.xml中配置Servlet 一、前端
<html>
<head>
<title>File Uploading Form</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>File Upload:</h3>
Select a file to upload: <br />
<form action="UploadServlet" method="post"
enctype="multipart/form-data">
<input type="file" name="file" size="50" />
<br />
<input type="submit" value="Upload File" />
</form>
</body>
</html>
二、书写Servlet
  web.xml// Import required java libraries
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
import javax.servlet.ServletConfig;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.apache.commons.fileupload.FileItem;
import org.apache.commons.fileupload.FileUploadException;
import org.apache.commons.fileupload.disk.DiskFileItemFactory;
import org.apache.commons.fileupload.servlet.ServletFileUpload;
import org.apache.commons.io.output.*;
public class UploadServlet extends HttpServlet {
private boolean isMultipart;
private String filePath;
private int maxFileSize = 50 * 1024;
private int maxMemSize = 4 * 1024;
private File file ;
public void init( ){
// Get the file location where it would be stored.
filePath =
getServletContext().getInitParameter("file-upload");
}
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, java.io.IOException {
// Check that we have a file upload request
isMultipart = ServletFileUpload.isMultipartContent(request);
response.setContentType("text/html");
java.io.PrintWriter out = response.getWriter( );
if( !isMultipart ){
out.println("<html>");
out.println("<head>");
out.println("<title>Servlet upload</title>");
out.println("</head>");
out.println("<body>");
out.println("<p>No file uploaded</p>");
out.println("</body>");
out.println("</html>");
return;
}
DiskFileItemFactory factory = new DiskFileItemFactory();
// maximum size that will be stored in memory
factory.setSizeThreshold(maxMemSize);
// Location to save data that is larger than maxMemSize.
factory.setRepository(new File("c:\\temp"));
// Create a new file upload handler
ServletFileUpload upload = new ServletFileUpload(factory);
// maximum file size to be uploaded.
upload.setSizeMax( maxFileSize );
try{
// Parse the request to get file items.
List fileItems = upload.parseRequest(request);
// Process the uploaded file items
Iterator i = fileItems.iterator();
out.println("<html>");
out.println("<head>");
out.println("<title>Servlet upload</title>");
out.println("</head>");
out.println("<body>");
while ( i.hasNext () )
{
FileItem fi = (FileItem)i.next();
if ( !fi.isFormField () )
{
// Get the uploaded file parameters
String fieldName = fi.getFieldName();
String fileName = fi.getName();
String contentType = fi.getContentType();
boolean isInMemory = fi.isInMemory();
long sizeInBytes = fi.getSize();
// Write the file
if( fileName.lastIndexOf("\\") >= 0 ){
file = new File( filePath +
fileName.substring( fileName.lastIndexOf("\\"))) ;
}else{
file = new File( filePath +
fileName.substring(fileName.lastIndexOf("\\")+1)) ;
}
fi.write( file ) ;
out.println("Uploaded Filename: " + fileName + "<br>");
}
}
out.println("</body>");
out.println("</html>");
}catch(Exception ex) {
System.out.println(ex);
}
}
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, java.io.IOException {
throw new ServletException("GET method used with " +
getClass( ).getName( )+": POST method required.");
}
} web.xml// Import required java libraries
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
import javax.servlet.ServletConfig;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.apache.commons.fileupload.FileItem;
import org.apache.commons.fileupload.FileUploadException;
import org.apache.commons.fileupload.disk.DiskFileItemFactory;
import org.apache.commons.fileupload.servlet.ServletFileUpload;
import org.apache.commons.io.output.*;
public class UploadServlet extends HttpServlet {
private boolean isMultipart;
private String filePath;
private int maxFileSize = 50 * 1024;
private int maxMemSize = 4 * 1024;
private File file ;
public void init( ){
// Get the file location where it would be stored.
filePath =
getServletContext().getInitParameter("file-upload");
}
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, java.io.IOException {
// Check that we have a file upload request
isMultipart = ServletFileUpload.isMultipartContent(request);
response.setContentType("text/html");
java.io.PrintWriter out = response.getWriter( );
if( !isMultipart ){
out.println("<html>");
out.println("<head>");
out.println("<title>Servlet upload</title>");
out.println("</head>");
out.println("<body>");
out.println("<p>No file uploaded</p>");
out.println("</body>");
out.println("</html>");
return;
}
DiskFileItemFactory factory = new DiskFileItemFactory();
// maximum size that will be stored in memory
factory.setSizeThreshold(maxMemSize);
// Location to save data that is larger than maxMemSize.
factory.setRepository(new File("c:\\temp"));
// Create a new file upload handler
ServletFileUpload upload = new ServletFileUpload(factory);
// maximum file size to be uploaded.
upload.setSizeMax( maxFileSize );
try{
// Parse the request to get file items.
List fileItems = upload.parseRequest(request);
// Process the uploaded file items
Iterator i = fileItems.iterator();
out.println("<html>");
out.println("<head>");
out.println("<title>Servlet upload</title>");
out.println("</head>");
out.println("<body>");
while ( i.hasNext () )
{
FileItem fi = (FileItem)i.next();
if ( !fi.isFormField () )
{
// Get the uploaded file parameters
String fieldName = fi.getFieldName();
String fileName = fi.getName();
String contentType = fi.getContentType();
boolean isInMemory = fi.isInMemory();
long sizeInBytes = fi.getSize();
// Write the file
if( fileName.lastIndexOf("\\") >= 0 ){
file = new File( filePath +
fileName.substring( fileName.lastIndexOf("\\"))) ;
}else{
file = new File( filePath +
fileName.substring(fileName.lastIndexOf("\\")+1)) ;
}
fi.write( file ) ;
out.println("Uploaded Filename: " + fileName + "<br>");
}
}
out.println("</body>");
out.println("</html>");
}catch(Exception ex) {
System.out.println(ex);
}
}
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, java.io.IOException {
throw new ServletException("GET method used with " +
getClass( ).getName( )+": POST method required.");
}
}
三、web.xml中配置上传文件存放地址
  web.xml<web-app>
....
<context-param>
<description>Location to store uploaded file</description>
<param-name>file-upload</param-name>
<param-value>
c:\apache-tomcat-5.5.29\webapps\data\
</param-value>
</context-param>
....
</web-app> web.xml<web-app>
....
<context-param>
<description>Location to store uploaded file</description>
<param-name>file-upload</param-name>
<param-value>
c:\apache-tomcat-5.5.29\webapps\data\
</param-value>
</context-param>
....
</web-app>
四、web.xml中配置Servlet
  web.xml<servlet>
<servlet-name>UploadServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>UploadServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>UploadServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/UploadServlet</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping> web.xml<servlet>
<servlet-name>UploadServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>UploadServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>UploadServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/UploadServlet</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
原文地址:http://www.tutorialspoint.com/servlets/servlets-file-uploading.htm
一个Servlet可以通过HTML表单标签将文件上传到服务器。支待上传的有文本、图像及任何文件。
创建文件上传表单:
下面的html代码创建了一个上传表单。创建过程需要注意以下几点:
l form标签中的method属性必须设置为POST,即GET方法是不可以的。
l form标签中的enctype属性应该设置为multipart/form-data。
l from标签中的action属性应该与服务器后台的servlet映射路径相同。接下来的实例,我们将使用UploadServlet实现文件上传。
l 要上传一个文件,你应该使用一个<input type=”file”.../>标记。要多个文件上传,必须包含多个具有不同的名称属性值的<input type=”file”.../>标记。The browser associates a Browse button with each of them。
|
<html>
<head>
<title>File Uploading Form</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>File Upload:</h3>
Select a file to upload: <br />
<form action="UploadServlet" method="post"
enctype="multipart/form-data">
<input type="file" name="file" size="50" />
<br />
<input type="submit" value="Upload File" />
</form>
</body>
</html>
|
以上代码将得到以下效果。你可以在本地PC上选择一个文件。当你点击“Upload File”,表单将会随着你选择的文件一起被提交。
后台servlet:
以下UploadServlet servlet将接收上传的文件并将其保存入<Tomcat-installation-directory>/webapps/data文件夹。这个文件夹的名称可以通过外部配置文件web.xml中的context-param元素内容增加。代码如下:
<web-app>
....
<context-param>
<description>Location to store uploaded file</description>
<param-name>file-upload</param-name>
<param-value>
c:"apache-tomcat-5.5.29"webapps"data"
</param-value>
</context-param>
....
</web-app>
|
以下是实现了多文件同时上传功能的UploadServlet。在此之前您必须确定以下几点:
l 以下实例依赖F ileUpload类,所以您须将最新版的commons-fileupload.x.x.jar放到您的classpath下。可以从这里下载:http://commons.apache.org/fileupload/。
l FileUpload类依赖于Commons IO包,所以您须将最新版commons-fileupload.x.x.jar放到您的classpath下。可以从这里下载:http://commons.apache.org/io/。
l 在测试以下例子的时候,您应该上传小于maxFileSize的文件,否则无法上传。
l 事先确定你已经建议好文件夹:c:"temp和c:"apache-tomcat-5.5.29"webapps"data。
// Import required java libraries
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
import javax.servlet.ServletConfig;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.apache.commons.fileupload.FileItem;
import org.apache.commons.fileupload.FileUploadException;
import org.apache.commons.fileupload.disk.DiskFileItemFactory;
import org.apache.commons.fileupload.servlet.ServletFileUpload;
import org.apache.commons.io.output.*;
public class UploadServlet extends HttpServlet {
private boolean isMultipart;
private String filePath;
private int maxFileSize = 50 * 1024;
private int maxMemSize = 4 * 1024;
private File file ;
public void init( ){
// Get the file location where it would be stored.
filePath =
getServletContext().getInitParameter("file-upload");
}
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, java.io.IOException {
// Check that we have a file upload request
isMultipart = ServletFileUpload.isMultipartContent(request);
response.setContentType("text/html");
java.io.PrintWriter out = response.getWriter( );
if( !isMultipart ){
out.println("<html>");
out.println("<head>");
out.println("<title>Servlet upload</title>");
out.println("</head>");
out.println("<body>");
out.println("<p>No file uploaded</p>");
out.println("</body>");
out.println("</html>");
return;
}
DiskFileItemFactory factory = new DiskFileItemFactory();
// maximum size that will be stored in memory
factory.setSizeThreshold(maxMemSize);
// Location to save data that is larger than maxMemSize.
factory.setRepository(new File("c:""temp"));
// Create a new file upload handler
ServletFileUpload upload = new ServletFileUpload(factory);
// maximum file size to be uploaded.
upload.setSizeMax( maxFileSize );
try{
// Parse the request to get file items.
List fileItems = upload.parseRequest(request);
// Process the uploaded file items
Iterator i = fileItems.iterator();
out.println("<html>");
out.println("<head>");
out.println("<title>Servlet upload</title>");
out.println("</head>");
out.println("<body>");
while ( i.hasNext () )
{
FileItem fi = (FileItem)i.next();
if ( !fi.isFormField () )
{
// Get the uploaded file parameters
String fieldName = fi.getFieldName();
String fileName = fi.getName();
String contentType = fi.getContentType();
boolean isInMemory = fi.isInMemory();
long sizeInBytes = fi.getSize();
// Write the file
if( fileName.lastIndexOf("""") >= 0 ){
file = new File( filePath +
fileName.substring( fileName.lastIndexOf(""""))) ;
}else{
file = new File( filePath +
fileName.substring(fileName.lastIndexOf("""")+1)) ;
}
fi.write( file ) ;
out.println("Uploaded Filename: " + fileName + "<br>");
}
}
out.println("</body>");
out.println("</html>");
}catch(Exception ex) {
System.out.println(ex);
}
}
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, java.io.IOException {
throw new ServletException("GET method used with " +
getClass( ).getName( )+": POST method required.");
}
}
|
编译并运行Servlet
编译以上UploadServlet并在web.xml中创建必须的实体,如下:
<servlet>
<servlet-name>UploadServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>UploadServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>UploadServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/UploadServlet</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
|
现在可以尝试使用你创建的HTML表单上传文件。当你访问http://localhost:8080/UploadFile.htm,浏览器里将会显示如下效果,您可以从本地上传你想要上传的任何文件。
如果您的servlet脚本运行成功,您的文件上传在c:"apache-tomcat-5.5.29"webapps"data"directory文件夹。
1、取得系统Properties,并配置 Properties props = System.getProperties();
props.setProperty("mail.transport.protocol", "smtp"); // smtp协议
props.setProperty("mail.smtp.host", m_server); // 服务器地址
props.setProperty("mail.smtp.port", "" + m_port); // 端口号 props.setProperty("mail.smtp.auth", "true"); //// 认证信息 2、将取得Session javax.mail.Session sess = javax.mail.Session.getDefaultInstance(props); 3、实例MimeMessage类,然后设置收件人、主题、发件日期 MimeMessage msg = new MimeMessage(sess); msg.setFrom(new InternetAddress(m_from)); // 发件人 msg.setRecipients(Message.RecipientType.TO, InternetAddress.parse(m_to)); //收件人 msg.setSubject(m_subject); //主题 msg.setSentDate(new Date()); //发件日期 4、向MimeMessage中添加文本内容及附件 MimeMultipart content = new MimeMultipart();// 文本内容 MimeBodyPart part = new MimeBodyPart(); //part还需要加入头,类型之类的属性 content.addBodyPart(part); part = new MimeBodyPart(); //这里是加入附件
FileDataSource fds = new FileDataSource(filename);
part.setDataHandler(new DataHandler(fds));
part.setFileName(MimeUtility.encodeText(fds.getName())); content.addBodyPart(part); msg.setContent(content); //设置并保存
msg.saveChanges(); 5、使用Session取得Transport Transport trans = sess.getTransport(); 6、使用Transport连接服务器 trans.connect(m_server, m_user, m_pass);
7、发送邮件并关闭 trans.sendMessage(msg, InternetAddress.parse(m_to));
trans.close();
1、java对象序列化不保存对象中的静态变量   serpublic class Test implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public static int staticVar = 5;
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
//初始时staticVar为5
ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream("result.obj"));
out.writeObject(new Test());
out.close();
//序列化后修改为10
Test.staticVar = 10;
ObjectInputStream oin = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(
"result.obj"));
Test t = (Test) oin.readObject();
oin.close();
//再读取,通过t.staticVar打印新的值
System.out.println(t.staticVar);//10
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} serpublic class Test implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public static int staticVar = 5;
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
//初始时staticVar为5
ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream("result.obj"));
out.writeObject(new Test());
out.close();
//序列化后修改为10
Test.staticVar = 10;
ObjectInputStream oin = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(
"result.obj"));
Test t = (Test) oin.readObject();
oin.close();
//再读取,通过t.staticVar打印新的值
System.out.println(t.staticVar);//10
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
2、虚拟机是否允许反序列化,不仅取决于类路径和功能代码是否一致,一个非常重要的一点是两个类的序列化 ID 是否一致(就是 private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L)。
3、父类的序列化与transient关键字
只有子类和父类都实现了Serializable接口时,对子类反序列化时才会将父类也序列化。反序列化过程是先反序列过父类对象再反序列化子类。而如果不想序列化某一个变量,则可以在定义变量时使用transient关键字。
  Parentimport java.io.Serializable;
public class Parent implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public int pi = 2;
public String pstr ="pstr";
public transient String ts ;
} Parentimport java.io.Serializable;
public class Parent implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public int pi = 2;
public String pstr ="pstr";
public transient String ts ;
}
  Son and mainimport java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Son extends Parent implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public int si = 1;
public String sstr = " sstr";
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
String path = "d:" + File.separator + "son.dll";
Son s = new Son();
s.si = 2;
s.pi = 2;
s.ts = "ts"; // ts在父类中的定义使用transient关键字
ObjectOutputStream op = null;
ObjectInputStream oi = null;
op = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(new File(path)));
op.writeObject(s);
op.close();
oi = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(path));
Son s1 = (Son) oi.readObject();
System.out.println("父类中的String pstr:" + s1.pstr);
System.out.println("父类中的int pi:" + s1.pi);
System.out.println("子类中的int si:" + s1.si);
System.out.println("父类中的transient String ts :" + s1.ts);//
}
} Son and mainimport java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Son extends Parent implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public int si = 1;
public String sstr = " sstr";
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
String path = "d:" + File.separator + "son.dll";
Son s = new Son();
s.si = 2;
s.pi = 2;
s.ts = "ts"; // ts在父类中的定义使用transient关键字
ObjectOutputStream op = null;
ObjectInputStream oi = null;
op = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(new File(path)));
op.writeObject(s);
op.close();
oi = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(path));
Son s1 = (Son) oi.readObject();
System.out.println("父类中的String pstr:" + s1.pstr);
System.out.println("父类中的int pi:" + s1.pi);
System.out.println("子类中的int si:" + s1.si);
System.out.println("父类中的transient String ts :" + s1.ts);//
}
}
4、Java 序列化机制为了节省磁盘空间,具有特定的存储规则,当写入文件的为同一对象时,并不会再将对象的内容进行存储,而只是再次存储一份引用。
从IBM DW 整理而来
http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/j-lo-serial/index.html#icomments
Class.froName(“cc.a.C”) 返回:C这个类的class(其实是这个类的字节码) 作用:告诉jvm使用相应的加载器,将C.class加载入jvm(至于加载到哪个位置,本人还不知道) 而Class.forName(“cc.a.C”).newInstance()则是实例化一个对象;而new关键的作用也是实例化一个对象 所以可以粗略的将这两种实例化对象的方法等同。 当然它们有不同的地方。 在网上看到别人是这样区别的: newInstance: 弱类型。低效率。只能调用无参构造。
new: 强类型。相对高效。能调用任何public构造。
将myeclipes安装目录C:\Program Files\Genuitec\Common\plugins 所有的东西复制到eclipes安装目录的\plugins里,并覆盖。 重新启动eclipes就可以了。
1、比较两个对象是否类型相同 array1.getClass().getName().equals(array2.getClass().getName() 2、倒置(reverse)数组中的元素 int i = 0;
int j = array.length - 1;
Object tmp;
while (j > i) {
tmp = array[j];
array[j] = array[i];
array[i] = tmp;
j--;
i++;
} 3、得到数组的容器类型 array.getClass().getComponentType(); 4、lastIndex()这类方法的实现 for (int i = startIndex; i >= 0; i--) {
if (objectToFind.equals(array[i])) {
return i;
}
} 5、isEmpty()这类方法的实现只要一句话,isNotEmpty方法依此推 return array == null || array.length == 0; 6、将两个数组合并addAll boolean[] joinedArray = new boolean[array1.length + array2.length];
System.arraycopy(array1, 0, joinedArray, 0, array1.length);
System.arraycopy(array2, 0, joinedArray, array1.length, array2.length); 7、将新元素加入到数组中 int arrayLength = Array.getLength(array);
Object newArray = Array.newInstance(array.getClass().getComponentType(), arrayLength + 1);
System.arraycopy(array, 0, newArray, 0, arrayLength);
return newArray; 8、获得数组长度的方法 int arrayLength = Array.getLength(array); 9、以反射的方式获得数组对象 Array.newInstance(array.getClass().getComponentType(), arrayLength + 1) 10、将某一元素从数组中移除 Object result = Array.newInstance(array.getClass().getComponentType(), getLength(array)- 1);
System.arraycopy(array, 0, result, 0, index);
if (index < length - 1) {
System.arraycopy(array, index + 1, result, index, length - index - 1);
}
1、泛型是给java编译器使用的,在源文件经过编译后,编译器会将类型信息去掉,所以   testList<String> ls = new ArrayList<String>();
List<Boolean> ls1 = new ArrayList<Boolean>();
System.out.println(ls==ls1) ;
//true; testList<String> ls = new ArrayList<String>();
List<Boolean> ls1 = new ArrayList<Boolean>();
System.out.println(ls==ls1) ;
//true;
2、可以绕过编译器的类型信息检查,而直接加入对象
  testimport java.util.* ;
import java.lang.* ;
public class Fanx {
public static void main (String args[]) {
ArrayList<Integer> ls = new ArrayList<Integer>();
try{
ls.getClass().getMethod("add", Object.class).invoke(ls,"abc") ;
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
System.out.println(ls.get(0));
}
}//out:abc testimport java.util.* ;
import java.lang.* ;
public class Fanx {
public static void main (String args[]) {
ArrayList<Integer> ls = new ArrayList<Integer>();
try{
ls.getClass().getMethod("add", Object.class).invoke(ls,"abc") ;
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
System.out.println(ls.get(0));
}
}//out:abc
3、泛型通配符
  testpublic static void printCollection(Collection<?> coll) {
//可以传Collection<String>,Collection<Integer>,Collection<Boolean>等等,但在此方法内不能使用诸如coll.add(“Strin”)这样具有类型信息的方法
for(Object obj:coll){
System.out.println(obj);
}//coll.add(“str”); 报错
} testpublic static void printCollection(Collection<?> coll) {
//可以传Collection<String>,Collection<Integer>,Collection<Boolean>等等,但在此方法内不能使用诸如coll.add(“Strin”)这样具有类型信息的方法
for(Object obj:coll){
System.out.println(obj);
}//coll.add(“str”); 报错
}
4、限定通配符上边界,限定通配符上边界
  testpublic static void printCollection1(Collection<? extends Number> coll) {
//
for(Object obj:coll){
System.out.println(obj);
}
}
//printCollection1(new ArrayList<Integer>()) ;//不报错
//printCollection1(new ArrayList<String>()) ; //报错,传入泛型参数必须为Number的子类 testpublic static void printCollection1(Collection<? extends Number> coll) {
//
for(Object obj:coll){
System.out.println(obj);
}
}
//printCollection1(new ArrayList<Integer>()) ;//不报错
//printCollection1(new ArrayList<String>()) ; //报错,传入泛型参数必须为Number的子类
  testpublic static void printCollection2(Collection<? super Number> coll) {
//
for(Object obj:coll){
System.out.println(obj);
}
}
//printCollection1(new ArrayList<Integer>()) ;//不报错
//printCollection1(new ArrayList<String>()) ; //报错,传的参数化必须是以Number为父类 testpublic static void printCollection2(Collection<? super Number> coll) {
//
for(Object obj:coll){
System.out.println(obj);
}
}
//printCollection1(new ArrayList<Integer>()) ;//不报错
//printCollection1(new ArrayList<String>()) ; //报错,传的参数化必须是以Number为父类
5、自定义泛型方法
  testpublic <T> T swap(T[] t,int i,int j){
T temp = t[i] ;
t[i] = t[j] ;
t[j] = t[i] ;
return (T) t ;
} testpublic <T> T swap(T[] t,int i,int j){
T temp = t[i] ;
t[i] = t[j] ;
t[j] = t[i] ;
return (T) t ;
}
6、类级别泛型
  testpublic class Dao<T> {
public <T> T getEntity(int id){
return null;
}
} testpublic class Dao<T> {
public <T> T getEntity(int id){
return null;
}
}
7、通过反射获得泛型的实际类型参数
  testimport java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Type;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Vector;
//假如我们要想获得 Vector<Date> v = new Vector<Date>(); v的实际类型参数
//我们必须写一个如applyRef的方法
public class Dao {
public void applyRef1(Map<String,Integer> map,Vector<Date> v){
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Method method = new Dao().getClass().getMethod("applyRef1", Map.class,Vector.class) ;
Type[] pType = method.getParameterTypes();
Type[] neiType = method.getGenericParameterTypes();
System.out.println(pType[0]) ;
System.out.println(pType[1]) ;
System.out.println(neiType[0]) ;
System.out.println(neiType[1]) ;
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} testimport java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Type;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Vector;
//假如我们要想获得 Vector<Date> v = new Vector<Date>(); v的实际类型参数
//我们必须写一个如applyRef的方法
public class Dao {
public void applyRef1(Map<String,Integer> map,Vector<Date> v){
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Method method = new Dao().getClass().getMethod("applyRef1", Map.class,Vector.class) ;
Type[] pType = method.getParameterTypes();
Type[] neiType = method.getGenericParameterTypes();
System.out.println(pType[0]) ;
System.out.println(pType[1]) ;
System.out.println(neiType[0]) ;
System.out.println(neiType[1]) ;
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
  Combinationsimport java.io.File;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Combinations implements Serializable{
/**
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 6509436857839528414L;
private int min;
private int max;
private char[] chars;// 字符数组
private int charLen;// 字符串长度
private String path ;
private String trueStr ;
private IOUtil iou;
public Combinations() {
this.min = 1;
this.max = trueStr.length() ;
this.charLen = trueStr.length();
this.chars = trueStr.toCharArray();
}
public Combinations(String str, int min, int max, String path) {
this.min = min;
this.max = max;
this.trueStr = str ;
this.charLen = str.length();
this.chars = str.toCharArray();
iou = IOUtil.getInstence(path);
}
public void combination() {
if (min > max) {
int t = max;
max = min;
min = t;
}
for (int i = min; i <= max; i++) {
combination(new StringBuffer(""), i);
}
}
public void combination(StringBuffer str, int length) {
if (length < 1) {
System.out.println("长度小于1");
}
if (length == 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < charLen; i++) {
StringBuffer result = new StringBuffer(str);
result.append(chars[i]);
iou.put(result.toString(),
MD5Util.getMD5Str(result.toString()));
}
}
if (length > 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < charLen; i++) {
StringBuffer temp = new StringBuffer(str);
combination(temp.append(chars[i]), length - 1);
}
}
}
/**
*setter getter
*/
public IOUtil getIou() {
return iou;
}
public void setIou(IOUtil iou) {
this.iou = iou;
}
public int getMin() {
return min;
}
public void setMin(int min) {
this.min = min;
}
public int getMax() {
return max;
}
public void setMax(int max) {
this.max = max;
}
public char[] getChars() {
return chars;
}
public void setChars(char[] chars) {
this.chars = chars;
}
public int getCharLen() {
return charLen;
}
public void setCharLen(int charLen) {
this.charLen = charLen;
}
public String getPath() {
return path;
}
public void setPath(String path) {
this.path = path;
}
public String getTrueStr() {
return trueStr;
}
public void setTrueStr(String trueStr) {
this.trueStr = trueStr;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "F:"+File.separator+"md5"
+File.separator+"md5.txt";
Combinations ct = new Combinations("123456",1,4,path);
ct.combination() ;
ct.getIou().close() ;
}
} Combinationsimport java.io.File;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Combinations implements Serializable{
/**
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 6509436857839528414L;
private int min;
private int max;
private char[] chars;// 字符数组
private int charLen;// 字符串长度
private String path ;
private String trueStr ;
private IOUtil iou;
public Combinations() {
this.min = 1;
this.max = trueStr.length() ;
this.charLen = trueStr.length();
this.chars = trueStr.toCharArray();
}
public Combinations(String str, int min, int max, String path) {
this.min = min;
this.max = max;
this.trueStr = str ;
this.charLen = str.length();
this.chars = str.toCharArray();
iou = IOUtil.getInstence(path);
}
public void combination() {
if (min > max) {
int t = max;
max = min;
min = t;
}
for (int i = min; i <= max; i++) {
combination(new StringBuffer(""), i);
}
}
public void combination(StringBuffer str, int length) {
if (length < 1) {
System.out.println("长度小于1");
}
if (length == 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < charLen; i++) {
StringBuffer result = new StringBuffer(str);
result.append(chars[i]);
iou.put(result.toString(),
MD5Util.getMD5Str(result.toString()));
}
}
if (length > 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < charLen; i++) {
StringBuffer temp = new StringBuffer(str);
combination(temp.append(chars[i]), length - 1);
}
}
}
/**
*setter getter
*/
public IOUtil getIou() {
return iou;
}
public void setIou(IOUtil iou) {
this.iou = iou;
}
public int getMin() {
return min;
}
public void setMin(int min) {
this.min = min;
}
public int getMax() {
return max;
}
public void setMax(int max) {
this.max = max;
}
public char[] getChars() {
return chars;
}
public void setChars(char[] chars) {
this.chars = chars;
}
public int getCharLen() {
return charLen;
}
public void setCharLen(int charLen) {
this.charLen = charLen;
}
public String getPath() {
return path;
}
public void setPath(String path) {
this.path = path;
}
public String getTrueStr() {
return trueStr;
}
public void setTrueStr(String trueStr) {
this.trueStr = trueStr;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "F:"+File.separator+"md5"
+File.separator+"md5.txt";
Combinations ct = new Combinations("123456",1,4,path);
ct.combination() ;
ct.getIou().close() ;
}
}
  md5Utilimport java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.security.MessageDigest;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
public class MD5Util {
/**
* MD5 加密
*/
public static String getMD5Str(String str) {
MessageDigest messageDigest = null;
try {
messageDigest = MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5");
messageDigest.reset();
messageDigest.update(str.getBytes("UTF-8"));
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
System.out.println("NoSuchAlgorithmException caught!");
System.exit(-1);
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
byte[] byteArray = messageDigest.digest();
StringBuffer md5StrBuff = new StringBuffer();
for (int i = 0; i < byteArray.length; i++) {
if (Integer.toHexString(0xFF & byteArray[i]).length() == 1)
md5StrBuff.append("0").append(
Integer.toHexString(0xFF & byteArray[i]));
else
md5StrBuff.append(Integer.toHexString(0xFF & byteArray[i]));
}
return md5StrBuff.toString();
}
} md5Utilimport java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.security.MessageDigest;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
public class MD5Util {
/**
* MD5 加密
*/
public static String getMD5Str(String str) {
MessageDigest messageDigest = null;
try {
messageDigest = MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5");
messageDigest.reset();
messageDigest.update(str.getBytes("UTF-8"));
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
System.out.println("NoSuchAlgorithmException caught!");
System.exit(-1);
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
byte[] byteArray = messageDigest.digest();
StringBuffer md5StrBuff = new StringBuffer();
for (int i = 0; i < byteArray.length; i++) {
if (Integer.toHexString(0xFF & byteArray[i]).length() == 1)
md5StrBuff.append("0").append(
Integer.toHexString(0xFF & byteArray[i]));
else
md5StrBuff.append(Integer.toHexString(0xFF & byteArray[i]));
}
return md5StrBuff.toString();
}
}
IO工具包
  md5Utilimport java.io.File;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
public class IOUtil implements Serializable {
/**
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1611785226109373473L;
/*
* 接收key 和 value,然后写入一个map,计数器count++如果count>30,IOWrite进入flush;
* 判断文件是否大于30MB,则新建另一文件将map清空,将count设置为0;
*/
private String sourcePath;
private String newPath;
private int MAXSIZE = 30000;
private int fileCount = 0; // 文件计数器
private PrintWriter pw = null;
private List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
private static IOUtil instance = new IOUtil();
private IOUtil() {
}
public static IOUtil getInstence(String path) {
if (null == instance) {
instance = new IOUtil();
}
instance.setSourcePath(path);
instance.setNewPath(path);
return instance;
}
public void put(String key, String value) {
//判断path中的文件
File file = new File(newPath) ;
if(!file.exists()){
try {
file.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}else{
}
try {
pw = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter(file));
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("找不到文件" + e.getMessage());
}
if (list.size() <= MAXSIZE) {
list.add(key + " " + value);
} else {
Iterator<String> it = list.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
pw.println(it.next());
}
// 刷新
pw.flush();
list.clear();
this.fileCount++;
this.newPath = this.sourcePath.substring(0, this.sourcePath
.lastIndexOf('.'))
+ "_"
+ this.fileCount
+ this.sourcePath.substring(this.sourcePath
.lastIndexOf('.'));
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void close() {
Iterator itor = null;
if (list.size() > 0 && this.pw != null) {
itor = list.iterator();
while (itor.hasNext()) {
pw.println(itor.next());
}
pw.close();
}
itor = null;
pw = null;
}
/*******************
* getter setter
*******************/
public String getSourcePath() {
return sourcePath;
}
public void setSourcePath(String sourcePath) {
this.sourcePath = sourcePath;
}
public String getNewPath() {
return newPath;
}
public void setNewPath(String newPath) {
this.newPath = newPath;
}
public PrintWriter getPw() {
return pw;
}
public void setPw(PrintWriter pw) {
this.pw = pw;
}
} md5Utilimport java.io.File;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
public class IOUtil implements Serializable {
/**
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1611785226109373473L;
/*
* 接收key 和 value,然后写入一个map,计数器count++如果count>30,IOWrite进入flush;
* 判断文件是否大于30MB,则新建另一文件将map清空,将count设置为0;
*/
private String sourcePath;
private String newPath;
private int MAXSIZE = 30000;
private int fileCount = 0; // 文件计数器
private PrintWriter pw = null;
private List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
private static IOUtil instance = new IOUtil();
private IOUtil() {
}
public static IOUtil getInstence(String path) {
if (null == instance) {
instance = new IOUtil();
}
instance.setSourcePath(path);
instance.setNewPath(path);
return instance;
}
public void put(String key, String value) {
//判断path中的文件
File file = new File(newPath) ;
if(!file.exists()){
try {
file.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}else{
}
try {
pw = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter(file));
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("找不到文件" + e.getMessage());
}
if (list.size() <= MAXSIZE) {
list.add(key + " " + value);
} else {
Iterator<String> it = list.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
pw.println(it.next());
}
// 刷新
pw.flush();
list.clear();
this.fileCount++;
this.newPath = this.sourcePath.substring(0, this.sourcePath
.lastIndexOf('.'))
+ "_"
+ this.fileCount
+ this.sourcePath.substring(this.sourcePath
.lastIndexOf('.'));
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void close() {
Iterator itor = null;
if (list.size() > 0 && this.pw != null) {
itor = list.iterator();
while (itor.hasNext()) {
pw.println(itor.next());
}
pw.close();
}
itor = null;
pw = null;
}
/*******************
* getter setter
*******************/
public String getSourcePath() {
return sourcePath;
}
public void setSourcePath(String sourcePath) {
this.sourcePath = sourcePath;
}
public String getNewPath() {
return newPath;
}
public void setNewPath(String newPath) {
this.newPath = newPath;
}
public PrintWriter getPw() {
return pw;
}
public void setPw(PrintWriter pw) {
this.pw = pw;
}
}
假设有一个Dog类
1、当首次创建Dog的对象时(构造器可以看成静态方法),或者Dog类的静态方法/静态域首次被访问时,java解释器必须查找类路径,以定位Dog.class文件
2、然后载入Dog.class,有关静态初始化的所有动作都会执行。因此,静态初始化的所有动作都会执行。因此,静态初始化只在Class对象首次加载的时候进行一次。
3、当用new Dog()创建对象的时候,首先将在堆上为Dog类分配足够的存储空间。
4、这块存储空间会被清零,这就看上去地将Dog对象中所有基本类型数据都设置成了默认值,而引用则被设置成了null。
5、执行所有出现于字段定义处的初始化动作。
6、执行构造器。
a、区分方法的重载有: 1、参数顺序 public void info(int i, String str); public void info(String str, int i); 2、以返回值区分重载方法 void f(){} int f(){return 1;} 当int i = f();时就会调用int f(){return i;}方法 b、基本类型的重载 1、基本类型从一个“较小”的类型自动提提升成“较大”的类型 2、如果找不到有char型的方法,就会把char型提升为int型
摘要: 这个类是用OSChina红薯老大的。
package com.dbutilTest;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.... 阅读全文
在spring配置文件中加入:   spring配置文件<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-2.5.xsd">
<context:annotation-config />
<context:component-scan base-package="cc.apl330" />
<bean
class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="locations">
<value>classpath:jdbc.properties</value>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="dataSource" destroy-method="close"
class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName"
value="${jdbc.driverClassName}" />
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" />
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />
</bean>
<bean id="sessionFactory"
class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.annotation.AnnotationSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
<!--
<property name="annotatedClasses">
<list>
<value>com.bjsxt.model.User</value>
<value>com.bjsxt.model.Log</value>
</list>
</property>
-->
<property name="packagesToScan">
<list>
<value>cc.apl330.model</value>
</list>
</property>
<property name="hibernateProperties">
<props>
<prop key="hibernate.dialect">
org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect
</prop>
<prop key="hibernate.show_sql">true</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="hibernateTemplate" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTemplate">
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory"></property>
</bean>
</beans> spring配置文件<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-2.5.xsd">
<context:annotation-config />
<context:component-scan base-package="cc.apl330" />
<bean
class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="locations">
<value>classpath:jdbc.properties</value>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="dataSource" destroy-method="close"
class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName"
value="${jdbc.driverClassName}" />
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" />
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />
</bean>
<bean id="sessionFactory"
class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.annotation.AnnotationSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
<!--
<property name="annotatedClasses">
<list>
<value>com.bjsxt.model.User</value>
<value>com.bjsxt.model.Log</value>
</list>
</property>
-->
<property name="packagesToScan">
<list>
<value>cc.apl330.model</value>
</list>
</property>
<property name="hibernateProperties">
<props>
<prop key="hibernate.dialect">
org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect
</prop>
<prop key="hibernate.show_sql">true</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="hibernateTemplate" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTemplate">
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
| jar包名称 | 所在位置 | 说明 | | antlr-2.7.6.jar | hibernate/lib/required | 解析HQL | | aspectjrt | spring/lib/aspectj | AOP | | aspectjweaver | .. | AOP | | cglib-nodep-2.1_3.jar | spring/lib/cglib | 代理,二进制增强 | | common-annotations.jar | spring/lib/j2ee | @Resource | | commons-collections-3.1.jar | hibernate/lib/required | 集合框架 | | commons-fileupload-1.2.1.jar | struts/lib | struts | | commons-io-1.3.2 | struts/lib | struts | | commons-logging-1.1.1 | 单独下载,删除1.0.4(struts/lib) | struts spring | | dom4j-1.6.1.jar | hibernate/required | 解析xml | | ejb3-persistence | hibernate-annotation/lib | @Entity | | freemarker-2.3.13 | struts/lib | struts | | hibernate3.jar | hibernate | | | hibernate-annotations | hibernate-annotation/ | | | hibernate-common-annotations | hibernate-annotation/lib | | | javassist-3.9.0.GA.jar | hiberante/lib/required | hibernate | | jta-1.1.jar | .. | hibernate transaction | | junit4.5 | | | | mysql- | | | | ognl-2.6.11.jar | struts/lib | | | slf4j-api-1.5.8.jar | hibernate/lib/required | hibernate-log | | slf4j-nop-1.5.8.jar | hibernate/lib/required | | | spring.jar | spring/dist | | | struts2-core-2.1.6.jar | struts/lib | | | xwork-2.1.2.jar | struts/lib | struts2 | | commons-dbcp | spring/lib/jarkata-commons | | | commons-pool.jar | .. | | | struts2-spring-plugin-2.1.6.jar | struts/lib | |
commons-fileupload-1.2.1.jar commons-io-1.3.2.jar commons-logging-1.1.jar freemarker-2.3.13.jar ognl-2.6.11.jar struts2-core-2.1.6.jar xwork-2.1.2.jar 以下是csdn下的下载链接: http://download.csdn.net/source/2907435
包括: antlr-2.7.6.jar commons-collections-3.1.jar dom4j-1.6.1.jar ejb3-persistence.jar hibernate3.jar hibernate-annotations.jar hibernate-commons-annotations.jar javassist-3.9.0.GA.jar jta-1.1.jar slf4j-api-1.5.8.jar slf4j-nop-1.5.8.jar 在csdn上的下载地址: http://download.csdn.net/source/2907437
<package name="member" namespace="/member" extends="struts-default">
<action name="regist" class="cc.apl330.action.MemberAction">
<result >/suc.jsp</result>
<result name="isExists">/fail.jsp</result>
</action>
</package> 运行正常,用户注册成功后会跳转到suc.jsp 如果将配置改成 <package name="member" namespace="/member" extends="struts-default">
<action name="regist" class="cc.apl330.action.MemberAction">
<result >/suc.html</result>
<result name="isExists">/fail.jsp</result>
</action>
</package> 运行不正常,用户输入数据后,点击确定。查看数据库,数据库写入正常,但页面空白,地址栏却正常:http://localhost:8080/test/member/regist
一、编写Servlet代码,继承自HttpServlet类,并覆盖 public void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) 方法   import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class SimpleHello extends HttpServlet {
@Override
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException {
PrintWriter out = resp.getWriter() ;
out.println("hello world");
out.close() ;
}
} import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class SimpleHello extends HttpServlet {
@Override
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException {
PrintWriter out = resp.getWriter() ;
out.println("hello world");
out.close() ;
}
}
二、部署Servlet。在web.xml中加入如下代码:
  <servlet>
<servlet-name>SimpleHello</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>cc.apl330.SimpleHello</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>SimpleHello</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/hello</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping> <servlet>
<servlet-name>SimpleHello</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>cc.apl330.SimpleHello</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>SimpleHello</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/hello</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
三、测试。在浏览器中输入:http://localhost:8080/ServletTest/hello
服务器过程是这样的:
1 服务器检测请求地址:http://localhost:8080/ServletTest/hello
2 得到字符串: /hello
3 在web.xml中寻找 <servlet-mapping>下的<url-pattern>内的值是否有对应的。有,就找到<servlet-name>的值
4 在web.xml中寻找 <servlet> 找到相应的servlet类执行
erji2.jsp 文件   <%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@page import="cc.apl330.Citys_Arr"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>My JSP 'erji2.jsp' starting page</title>
</head>
<!-- init()用于初始化联动选项 -->
<body onload="init()">
<%
//读取数据
Citys_Arr ca = null ;
%>
<form action="" name="fom">
<select name="s1" onchange="sel()">
<%
ca = new Citys_Arr() ;
for(int i = 0 ; i < ca.getCitys().length; i++ ) {
%>
<option><%=ca.getCitys()[i]%></option>
<%
}
%>
</select>
<select name="s2">
</select>
</form>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
<%
int citys = ca.getCitys().length ;
%>
var select2 = new Array(<%=citys%>) ;
<!-- //初始化 -->
function init() {
<%
for(int i = 0 ; i < citys ; i++ ) {
%>
select2[<%=i%>] = new Array() ;
<%
}
%>
<%
for(int x = 0 ; x < citys ;x++){
for(int y = 0 ; y < ca.getZone()[u].length ; y++){
%>
select2[<%=x%>][<%=y%>] = new Option("<%=ca.getZone()[x][y]%>" ,
"<%=ca.getZone()[x][y]%>");
<%
}
}
%>
}
<!-- //根据前一项选择加载联动数据 -->
function sel() {
var pp = document.fom.s1.options.selectedIndex ;
var temp = document.fom.s2;
for (i = 0; i < select2[pp].length; i++) {
temp.options[i] = new Option(select2[pp][i].text,
select2[pp][i].value);
}
temp.options[0].selected = true;
}
</script>
</html> <%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@page import="cc.apl330.Citys_Arr"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>My JSP 'erji2.jsp' starting page</title>
</head>
<!-- init()用于初始化联动选项 -->
<body onload="init()">
<%
//读取数据
Citys_Arr ca = null ;
%>
<form action="" name="fom">
<select name="s1" onchange="sel()">
<%
ca = new Citys_Arr() ;
for(int i = 0 ; i < ca.getCitys().length; i++ ) {
%>
<option><%=ca.getCitys()[i]%></option>
<%
}
%>
</select>
<select name="s2">
</select>
</form>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
<%
int citys = ca.getCitys().length ;
%>
var select2 = new Array(<%=citys%>) ;
<!-- //初始化 -->
function init() {
<%
for(int i = 0 ; i < citys ; i++ ) {
%>
select2[<%=i%>] = new Array() ;
<%
}
%>
<%
for(int x = 0 ; x < citys ;x++){
for(int y = 0 ; y < ca.getZone()[u].length ; y++){
%>
select2[<%=x%>][<%=y%>] = new Option("<%=ca.getZone()[x][y]%>" ,
"<%=ca.getZone()[x][y]%>");
<%
}
}
%>
}
<!-- //根据前一项选择加载联动数据 -->
function sel() {
var pp = document.fom.s1.options.selectedIndex ;
var temp = document.fom.s2;
for (i = 0; i < select2[pp].length; i++) {
temp.options[i] = new Option(select2[pp][i].text,
select2[pp][i].value);
}
temp.options[0].selected = true;
}
</script>
</html>
Citys_Arr.java //用于读取数据
  package cc.apl330;
public class Citys_Arr {
private String[] citys = {"桂林","崇左"} ;
private String[][] zone = {
{"平乐","临桂","荔浦","二塘"},
{"龙州","天等","花山","乐一"}
} ;
public String[] getCitys() {
return citys;
}
public void setCitys(String[] citys) {
this.citys = citys;
}
public String[][] getZone() {
return zone;
}
public void setZone(String[][] zone) {
this.zone = zone;
}
} package cc.apl330;
public class Citys_Arr {
private String[] citys = {"桂林","崇左"} ;
private String[][] zone = {
{"平乐","临桂","荔浦","二塘"},
{"龙州","天等","花山","乐一"}
} ;
public String[] getCitys() {
return citys;
}
public void setCitys(String[] citys) {
this.citys = citys;
}
public String[][] getZone() {
return zone;
}
public void setZone(String[][] zone) {
this.zone = zone;
}
}
1)将公共操作和域放置在超类 2)不要使用受保护的域 3)使用继承实现“is-a”关系 4)除非所有继承的方法都有意义,否则不要使用继承 5)在覆盖方法的时候,不要心迹预期的行为 6)使用多态,而非类型信息 7)不要过多地使用反射
  public class Person{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p1 = new Person("p1","femail",15) ;
Person p2 = new Person("p","mail", 20) ;
Person p3 = new Person("p","mail", 20) ;
System.out.println(p1.equals(p2)) ;
System.out.println(p3.equals(p2)) ;
}
public Person() {} ;
public Person(String name, String sex, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
this.age = age;
}
public boolean equals(Object otherObject) {
//检测两个引用是否指向同一对象
if( this == otherObject ) return true ;
//检测otherObject是否为空
if( null == otherObject) return false ;
//检测是否为同一个类
if( getClass() != otherObject.getClass() ) return false ;
//将otherObject转成Person类
Person person = (Person)otherObject ;
return this.getName().equals(person.getName())
&& this.getSex().equals(person.getSex())
&& this.getAge() == person.getAge() ;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String name = null;
public String sex = null ;
public int age = 0 ;
} public class Person{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p1 = new Person("p1","femail",15) ;
Person p2 = new Person("p","mail", 20) ;
Person p3 = new Person("p","mail", 20) ;
System.out.println(p1.equals(p2)) ;
System.out.println(p3.equals(p2)) ;
}
public Person() {} ;
public Person(String name, String sex, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
this.age = age;
}
public boolean equals(Object otherObject) {
//检测两个引用是否指向同一对象
if( this == otherObject ) return true ;
//检测otherObject是否为空
if( null == otherObject) return false ;
//检测是否为同一个类
if( getClass() != otherObject.getClass() ) return false ;
//将otherObject转成Person类
Person person = (Person)otherObject ;
return this.getName().equals(person.getName())
&& this.getSex().equals(person.getSex())
&& this.getAge() == person.getAge() ;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String name = null;
public String sex = null ;
public int age = 0 ;
}
equals方法具有以下特性: 1)自反性:对于任何非空引用 x ,x.equals(x) 应该返回 true。 2)对称性:对于任何引用 x 和 y ,如果 x.equals(y)返回 true ,那么 y.equals(x) 也应该返回 true 。 3)传递性:对于任何引用 x 、y 和 z ,如果 x.equals(y) 返回 true ,y.equals(z) 返回 true ,那么 x.equals(z) 就应该返回 true 。 4)一致性:如果 x 和 y 引用的对象没有发生变化,那么反复调用 x.equals(y) 应该返回同样的结果。 5)对于任意非空引用 x ,x.equals(null) 应该返回false 。
次序为: 1、static块内代码 2、自上而下的运行代码 3、在try{}catch(){}finally{}内,在try{}内遇到return关键字的时候,就马上跳到finally块内执行。4、执行完毕finally{}块后就执行刚才的return语句注意:finally内有return后,方法的其他地方就不能存在return。   public class Main {
static{
System.out.println("static");
}
public int test(){
try{
System.out.println("try") ;
return 1 ;
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage()) ;
}finally{
System.out.println("finally") ;
}
return 3 ;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = new Main().test() ;
System.out.println("test:" + i );
}
}
public class Main {
static{
System.out.println("static");
}
public int test(){
try{
System.out.println("try") ;
return 1 ;
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage()) ;
}finally{
System.out.println("finally") ;
}
return 3 ;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = new Main().test() ;
System.out.println("test:" + i );
}
}
输出结果为: static
try
finally
test:1
package cc.apl330;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import cc.apl330.dao.UserDAOException;
//注意批处理在实际中应用要注意同时打包太多的处理会引起内存溢出.
public class BatchTest {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis() ;
//常规方式提交处理
for(int i=0; i<200; i++){
create(i) ;
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis() ;
System.out.println("crate:" + (end - start)) ;
//成批提交处理
start = System.currentTimeMillis() ;
create1() ;
end = System.currentTimeMillis() ;
System.out.println("Batchcrate:" + (end - start)) ;
}
//常规方式提交处理
static void create(int i){
String sql = "INSERT INTO USER(name,money) VALUES(?,?);";
Connection conn;
PreparedStatement ps;
try {
conn = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql) ;
ps.setString(1, "name"+i) ;
ps.setFloat(2, 200f+i) ;
ps.executeUpdate();
JdbcUtil.free(null, ps, conn) ;
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new UserDAOException(e.getMessage(),e) ;
}
}
//成批提交处理
static void create1(){
String sql = "INSERT INTO USER(name,money) VALUES(?,?);";
Connection conn;
PreparedStatement ps;
try {
conn = JdbcUtil.getConnection();
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql) ;
for(int i=200; i<400; i++){
ps.setString(1, "name"+i) ;
ps.setFloat(2, 200f+i) ;
ps.addBatch();//将处理打包
}
//执行批处理
int[] is = ps.executeBatch() ;
System.out.println(is.length+"") ;
JdbcUtil.free(null, ps, conn) ;
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new UserDAOException(e.getMessage(),e) ;
}
}
}
第一个JAVA程序: public class Hello{
public static void main(String[] args ){
System.out.println("hello world") ;
}
} 使用文本编辑器输入以上内容,保存为java源文件扩展名:Hello.java
需要注意以下几点:
JAVA对大小写敏感(main 与 Main 代表不同的概念)
源代码的文件名必须与公有类的名字相同,并用.java作为扩展名
类的标准命名规范:类名是以大写字母开关的名词。
程序总是从main方法开始运行
一对花括号表示方法的开始与结束语。程序中每条语句都以分号结束(就算分号前没有写任何,一个分号也算一句语句)。
点号用来调用一个方法如 System.out.println() ;println()是一个方法。方法后的括号是必须,即便里什么也没有。 3.2 注释
单行注释: //
多行注释: /**/
第三种注释:以/**开始 以*/结束。这种注释用来自动生成文档 单行注释,注释内容从//开始到本行结尾
多行注释内不能再包括 /**/。意思是他们不能嵌套 3.3数据类型
java是一种强类型语言。这就意味每一个变量声明一种类型。
数据类型的大小与运行代码的机器无关。
java一共有8种基本类型,4个整型,2个浮点类型,1个char类型,1个boolean类型(表示真假)
整型
整型又按照长度分为4种:int(4 byte) short(2 byte) long(8 byte) byte(1 byte)
使用long类型需要加后缀L(400000000L),十六进制数值有一个前缀0x(如0xCAFE),八进制有一个前缀0(如010对应八进制中的8,建议不要使用八进制常数,因为他比较容易混淆)
浮点型
浮点类型有两种:float(4 byte) double(8 byte)
浮点类型有一个后缀F(如2.12F),没有加后缀的(如2.12)默认为double类型,double后缀为D。
使用浮点类型需要注意:浮点数的计算会有误差。用2.0-1.1不会得到0.9,有可能得到0.89999。原因是浮点数点值是采用二进制系统表示的,而在二进制里无法精确的表示分数1/10。就像二进制无法精确的表示1/3一样。如果需要在数值计算中不含舍入误差,就应该使用BigDecimal类。
char类型
在程序设计中尽量不要使用此类型
boolean类型
boolean(布尔)类型有两个值:flase 和 true ; 这两个值不能和整型相互转换。
3.4变量
声明变量方式为:
double salary;
int vacat ;
long earth ;
变量名必须是一个公字母开关的字母或数字序列。但,变量名命名不能为java保留字。
3.4.1 初始化变量
int i ; //申明变量i
i = 1 ; //给变量i赋值
也可以这样赋值 int y = 10 ;
3.4.2 常量
关键字final用于声明常量。常量只能被赋值一次。一旦被赋值之后,就不能够再更改了。习惯上常量名使用大写。
有一种常量叫类常量,这种常量可以在各个类之间使用。定义方法: static final int sf = 90 ;
实例:
Changliang.java
public class Changliang {
static final int ZHAI = 90 ;
}
IOtest.java
public class IOtest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Changliang.ZHAI + "") ;
}
} 3.5 运算符
JAVA中运算符包括:+(加)-(减)*(乘)/(除)%(取模或者叫求余)
/ 号两边如果是整型,运算的结果会截去小数点后的数字。如 15/2=7。如果是浮点型则是这样15.0/2=7.5 。
% 符使用如15%2=1
为简化编程,JAVA像C语言一样有两元运算符。
如{int i = 1 ;i = i+2 ;}可以简化为{int i = 1; i += 2;}
3.5.1自增自减
以下源码便说明:
IOtest.java
public class IOtest {
public strictfp static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("i++,是先用后加。当然是在同一语句中") ;
int i = 1 ;
int y = 4 * i++ ;
System.out.println("i=" + i) ;
System.out.println("y=" + y) ;
System.out.println("++i,是先加后用。当然是在同一语句中") ;
i =1 ;
int x = 4 * ++i ;
System.out.println("i=" + i) ;
System.out.println("x=" + x) ;
//
// i++,是先用后加。当然是在同一语句中
// i=2
// y=4
// ++i,是先加后用。当然是在同一语句中
// i=2
// x=8
//以下使用自增自减的效果是一样的
int p = 1 ;
System.out.println("p="+ p) ;
p++ ;
System.out.println("p="+ p) ;
int q = 1 ;
System.out.println("q="+ q) ;
q++ ;
System.out.println("q="+ q) ;
// p=1
// p=2
// q=1
// q=2
}
}
运行主类
Main.java
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new ActionInterceptor().invoke() ;
}
} /********************************/ 拦截器核心
ActionInterceptor.java import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List; public class ActionInterceptor {
List<Inte> intes = new ArrayList<Inte>() ;
int index = -1 ;
public ActionInterceptor() {
intes.add(new FistInte()) ;
intes.add(new SecondInte()) ;
}
public void invoke() {
index++ ;
if(index >= intes.size()) {
new Action().execute() ;
}else {
this.intes.get(index).inte(this) ;
}
}
} /********************************/ 接口:与拦截器之间的通讯接口
Inte.java public interface Inte {
void inte(ActionInterceptor actioninterceptor) ;
} /********************************/ 接口使用类
FistInte.java
public class FistInte implements Inte { @Override
public void inte(ActionInterceptor actioninterceptor) {
System.out.println(1) ;
actioninterceptor.invoke() ;
System.out.println(-1) ;
}
} SecondInte.java
public class SecondInte implements Inte { @Override
public void inte(ActionInterceptor actioninterceptor) {
System.out.println(2) ;
actioninterceptor.invoke() ;
System.out.println(-2) ;
}
} /********************************/ 动作类 Action.java
public class Action {
public void execute() {
System.out.println("execute!") ;
}
}
|