最近由于项目的需要,研究了一下SWT的Accessibility。关于Accessibility,这是一个很难缠的search,给残疾人用的东东,正常人基本上不会用到,网上文章少之又少。可以查阅到的一篇来自于IBM developerWorks的文章:使用 Eclipse 创建易访问的应用程序:介绍
易访问性是一个总括的术语,它包括生成使具有各种残疾的人易用的产品所涉及的所有东西和人。美国已经立法,不符合Accessibility规范的软件不能够在政府部门销售。在美国,创建易访问的应用程序的主要商业(对比人道主义)驱动力是 Rehabilitation Act 1998 年的修正法案,称为 Section 508。Section 508 要求联邦机构使他们的信息技术对带有残疾的人易于访问。
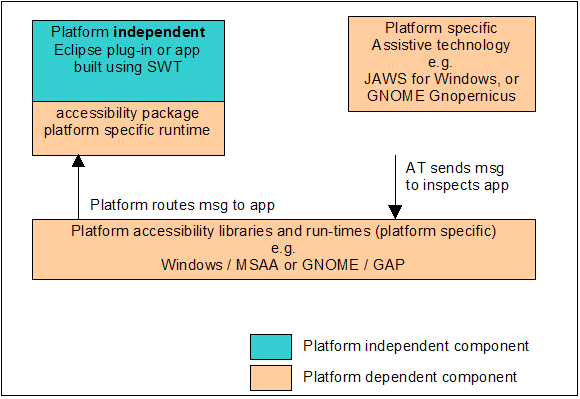
Eclipse 拥有一个包含 API:org.eclipse.swt.accessibility 的易访问性包。Eclipse 3.0 易访问性特征是基于 MSAA 1.3 程序设计模型所提供的功能。您可以将 Eclipse 中的 Accessible 对象联系到每个控件上,并且 org.eclipse.swt.accessibility 接口中的方法集对应 MSAA 1.3 IAccessible 界面中的消息集。
org.eclipse.swt.accessibility 的接口:
| Interface Summary |
| AccessibleControlListener |
Classes that implement this interface provide methods that deal with the events that are generated when an accessibility client sends a message to a control. |
| AccessibleListener |
Classes that implement this interface provide methods that deal with the events that are generated when an accessibility client sends a message to a control. |
| AccessibleTextListener |
Classes that implement this interface provide methods that deal with the events that are generated when an accessibility client sends a message to a control. |
SWT 自身包含的控件中只有寥寥几个用到了Accessibility,JFace里也不多。看了所有的Accessibility相关代码,只能总结一部分规律:
- 一般的复杂控件是没有必要定义Accessibility的。
- 如果是模拟实现一个比较简单的基本控件,比如Combo,Label,Spinner等,有必要定义Accessibility。
- 所有的自定义控件都要实现AccessibleControlListener接口。
- 所有的包含文本框的控件都要实现AccessibleTextListener接口。
- 设置AccessibleListener的getHelp( )最好是给控件加上Tooltip,因为Wineyes这些屏幕阅读器阅读都是根据Tooltip,无视getHelp( )的设置。
- 设置AccessibleListener的getName( ),一般来说,可以设置为这个控件相关联的Label的Text或者该控件上的某部分文字,自己斟酌考虑设置。
- getKeyboardShortcut( ),考虑控件的快捷操作方式,如果需要的话。
以下是CCombo的Accessibility代码:
void initAccessible() {
AccessibleAdapter accessibleAdapter = new AccessibleAdapter () {
publicvoid getName (AccessibleEvent e) {
String name = null;
Label label = getAssociatedLabel ();
if (label != null) {
name = stripMnemonic (label.getText());
}
e.result = name;
}
publicvoid getKeyboardShortcut(AccessibleEvent e) {
String shortcut = null;
Label label = getAssociatedLabel ();
if (label != null) {
String text = label.getText ();
if (text != null) {
char mnemonic = _findMnemonic (text);
if (mnemonic != '\0') {
shortcut = "Alt+"+mnemonic;
}
}
}
e.result = shortcut;
}
publicvoid getHelp (AccessibleEvent e) {
e.result = getToolTipText ();
}
};
getAccessible ().addAccessibleListener (accessibleAdapter);
text.getAccessible ().addAccessibleListener (accessibleAdapter);
list.getAccessible ().addAccessibleListener (accessibleAdapter);
arrow.getAccessible ().addAccessibleListener (new AccessibleAdapter() {
publicvoid getName (AccessibleEvent e) {
e.result = isDropped () ? SWT.getMessage ("SWT_Close") : SWT.getMessage ("SWT_Open");
}
publicvoid getKeyboardShortcut (AccessibleEvent e) {
e.result = "Alt+Down Arrow";
}
publicvoid getHelp (AccessibleEvent e) {
e.result = getToolTipText ();
}
});
getAccessible().addAccessibleTextListener (new AccessibleTextAdapter() {
publicvoid getCaretOffset (AccessibleTextEvent e) {
e.offset = text.getCaretPosition ();
}
publicvoid getSelectionRange(AccessibleTextEvent e) {
Point sel = text.getSelection();
e.offset = sel.x;
e.length = sel.y - sel.x;
}
});
getAccessible().addAccessibleControlListener (new AccessibleControlAdapter() {
publicvoid getChildAtPoint (AccessibleControlEvent e) {
Point testPoint = toControl (e.x, e.y);
if (getBounds ().contains (testPoint)) {
e.childID = ACC.CHILDID_SELF;
}
}
publicvoid getLocation (AccessibleControlEvent e) {
Rectangle location = getBounds ();
Point pt = toDisplay (location.x, location.y);
e.x = pt.x;
e.y = pt.y;
e.width = location.width;
e.height = location.height;
}
publicvoid getChildCount (AccessibleControlEvent e) {
e.detail = 0;
}
publicvoid getRole (AccessibleControlEvent e) {
e.detail = ACC.ROLE_COMBOBOX;
}
publicvoid getState (AccessibleControlEvent e) {
e.detail = ACC.STATE_NORMAL;
}
publicvoid getValue (AccessibleControlEvent e) {
e.result = getText ();
}
});
text.getAccessible ().addAccessibleControlListener (new AccessibleControlAdapter () {
publicvoid getRole (AccessibleControlEvent e) {
e.detail = text.getEditable () ? ACC.ROLE_TEXT : ACC.ROLE_LABEL;
}
});
arrow.getAccessible ().addAccessibleControlListener (new AccessibleControlAdapter() {
publicvoid getDefaultAction (AccessibleControlEvent e) {
e.result = isDropped () ? SWT.getMessage ("SWT_Close") : SWT.getMessage ("SWT_Open");
}
});
}
在SWT控件中,包含Accessibility功能的控件有:CCombo,CLabel,CTableFolder,StyledText。