 2006年10月8日
2006年10月8日
MyEclipse5.5推出有一段时间了,但是网上一直都没有破解的文件,通过今天跟公司几个同事的努力尝试终于找到破解的方法了,说起来比较可笑,我们经过好多次的尝试,最后用MyEclipse4.1的破解文件就可以破解MyEclipse5.5了,我们用的MyEclipse5.5的版本是MyEclipse_5.5M2_E3.2.2,Eclipse的版本是eclipse3.2.2大家可以尝试一下.
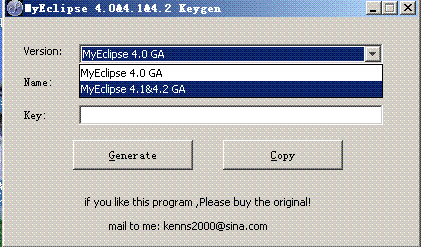
在此特别要说明一下的是运行MyEclipse4.1的时候要选择MyEclipse4.1&4.2 GA这个选择才可以破解如图
MyEclipse_5.5M2_E3.2.2的官方下载地址 : http://www.myeclipseide.com/ContentExpress-display-ceid-110.html
MyEclipse4.1破解文件下载
最近在用eclipse的时候,过上一会老弹出一个对话框,提示内存不足(大意),找了好多资料都没有解决,最近在eclipse的官方网站上找到了其解决的办法,希望对像我一样的朋友有帮助,解决方法如下,
在桌面上建一个启动eclipse的快捷方式,在该快捷方式上单击右键,在常规标签的目标中加入下面的内容:
E:\eclipse\eclipse.exe -clean -vmargs -Xms128M -Xmx512M -XX:PermSize=64M -XX:MaxPermSize=128M,其中“E:\eclipse\eclipse.exe” 是我eclipse的路径。
然后重启你的eclipse试试!
在IIS中 发布程序一个ASP.NET程序,通过IE访问报如下错误:
当前标识(NT AUTHORITY\NETWORK SERVICE)没有对“C:\WINDOWS\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v2.0.50727\Temporary ASP.NET Files”的写访问权限。
说明: 执行当前 Web 请求期间,出现未处理的异常。请检查堆栈跟踪信息,以了解有关该错误以及代码中导致错误的出处的详细信息。
异常详细信息: System.Web.HttpException: 当前标识(NT AUTHORITY\NETWORK SERVICE)没有对“C:\WINDOWS\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v2.0.50727\Temporary ASP.NET Files”的写访问权限。
翻阅了一些资料后发现是需要重新注册IIS服务扩展, 解决方法如下:
在“开始”-“运行”里输入如入命令,回车,搞定
C:\WINDOWS\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v2.0.50727\aspnet_regiis -i -enable
摘要: 9.8 Struts
与
...
阅读全文
称呼
Functions
标签库为标签库,倒不如称呼其为函数库来得更容易理解些。因为
Functions
标签库并没有提供传统的标签来为
JSP
页面的工作服务,而是被用于
EL
表达式语句中。在
JSP2.0
规范下出现的
Functions
标签库为
EL
表达式语句提供了许多更为有用的功能。
Functions
标签库分为两大类,共
16
个函数。
q
长度函数:
fn:length
q
字符串处理函数:
fn:contains
、
fn:containsIgnoreCase
、
fn:endsWith
、
fn:escapeXml
、
fn:indexOf
、
fn:join
、
fn:replace
、
fn:split
、
fn:startsWith
、
fn:substring
、
fn:substringAfter
、
fn:substringBefore
、
fn:toLowerCase
、
fn:toUpperCase
、
fn:trim
以下是各个函数的用途和属性以及简单示例。
9.7.1
长度函数
fn:length
函数
长度函数
fn:length
的出现有重要的意义。在
JSTL1.0
中,有一个功能被忽略了,那就是对集合的长度取值。虽然
java.util.Collection
接口定义了
size
方法,但是该方法不是一个标准的
JavaBean
属性方法(没有
get,set
方法),因此,无法通过
EL
表达式“
${collection.size}
”来轻松取得。
fn:length
函数正是为了解决这个问题而被设计出来的。它的参数为
input
,将计算通过该属性传入的对象长度。该对象应该为集合类型或
String
类型。其返回结果是一个
int
类型的值。下面看一个示例。
<%ArrayList arrayList1 = new ArrayList();
arrayList1.add("aa");
arrayList1.add("bb");
arrayList1.add("cc");
%>
<%request.getSession().setAttribute("arrayList1", arrayList1);%>
${fn:length(sessionScope.arrayList1)}
假设一个
ArrayList
类型的实例“
arrayList1
”,并为其添加三个字符串对象,使用
fn:length
函数后就可以取得返回结果为“
3
”。
9.7.2
判断函数
fn:contains
函数
fn:contains
函数用来判断源字符串是否包含子字符串。它包括
string
和
substring
两个参数,它们都是
String
类型,分布表示源字符串和子字符串。其返回结果为一个
boolean
类型的值。下面看一个示例。
${fn:contains("ABC", "a")}<br>
${fn:contains("ABC", "A")}<br>
前者返回“
false
”,后者返回“
true
”。
fn:containsIgnoreCase
函数与
fn:contains
函数的功能差不多,唯一的区别是
fn:containsIgnoreCase
函数对于子字符串的包含比较将忽略大小写。它与
fn:contains
函数相同,包括
string
和
substring
两个参数,并返回一个
boolean
类型的值。下面看一个示例。
${fn:containsIgnoreCase("ABC", "a")}<br>
${fn:containsIgnoreCase("ABC", "A")}<br>
前者和后者都会返回“
true
”。
9.7.4
词头判断函数
fn:startsWith
函数
fn:startsWith
函数用来判断源字符串是否符合一连串的特定词头。它除了包含一个
string
参数外,还包含一个
subffx
参数,表示词头字符串,同样是
String
类型。该函数返回一个
boolean
类型的值。下面看一个示例。
${fn:startsWith ("ABC", "ab")}<br>
${fn:startsWith ("ABC", "AB")}<br>
前者返回“
false
”,后者返回“
true
”。
9.7.5
词尾判断函数
fn:endsWith
函数
fn:endsWith
函数用来判断源字符串是否符合一连串的特定词尾。它与
fn:startsWith
函数相同,包括
string
和
subffx
两个参数,并返回一个
boolean
类型的值。下面看一个示例。
${fn:endsWith("ABC", "bc")}<br>
${fn:endsWith("ABC", "BC")}<br>
前者返回“
false
”,后者返回“
true
”。
9.7.6
字符实体转换函数
fn:escapeXml
函数
fn:escapeXml
函数用于将所有特殊字符转化为字符实体码。它只包含一个
string
参数,返回一个
String
类型的值。
9.7.8
字符匹配函数
fn:indexOf
函数
fn:indexOf
函数用于取得子字符串与源字符串匹配的开始位置,若子字符串与源字符串中的内容没有匹配成功将返回“
-1
”。它包括
string
和
substring
两个参数,返回结果为
int
类型。下面看一个示例。
${fn:indexOf("ABCD","aBC")}<br>
${fn:indexOf("ABCD","BC")}<br>
前者由于没有匹配成功,所以返回
-1
,后者匹配成功将返回位置的下标,为
1
。
9.7.9
分隔符函数
fn:join
函数
fn:join
函数允许为一个字符串数组中的每一个字符串加上分隔符,并连接起来。它的参数、返回结果和描述如表
9.25
所示:
表
9.25
fn:join
函数
|
参数
|
描述
|
|
array
|
字符串数组。其类型必须为
String[]
类型
|
|
separator
|
分隔符。其类型必须为
String
类型
|
|
返回结果
|
返回一个
String
类型的值
|
下面看一个示例。
<% String[] stringArray = {"a","b","c"}; %>
<%request.getSession().setAttribute("stringArray", stringArray);%>
${fn:join(sessionScope.stringArray,";")}<br>
定义数组并放置到
Session
中,然后通过
Session
得到该字符串数组,使用
fn:join
函数并传入分隔符“
;
”,得到的结果为“
a;b;c
”。
9.7.10
替换函数
fn:replace
函数
fn:replace
函数允许为源字符串做替换的工作。它的参数、返回结果和描述如表
9.26
所示:
表
9.26
fn:replace
函数
|
参数
|
描述
|
|
inputString
|
源字符串。其类型必须为
String
类型
|
|
beforeSubstring
|
指定被替换字符串。其类型必须为
String
类型
|
|
afterSubstring
|
指定替换字符串。其类型必须为
String
类型
|
|
返回结果
|
返回一个
String
类型的值
|
下面看一个示例。
${fn:replace("ABC","A","B")}<br>
将“
ABC
”字符串替换为“
BBC
”,在“
ABC
”字符串中用“
B
”替换了“
A
”。
9.7.11
分隔符转换数组函数
fn:split
函数
fn:split
函数用于将一组由分隔符分隔的字符串转换成字符串数组。它的参数、返回结果和描述如表
9.27
所示:
表
9.27
fn:split
函数
|
参数
|
描述
|
|
string
|
源字符串。其类型必须为
String
类型
|
|
delimiters
|
指定分隔符。其类型必须为
String
类型
|
|
返回结果
|
返回一个
String[]
类型的值
|
下面看一个示例。
${fn:split("A,B,C",",")}<br>
将“
A,B,C
”字符串转换为数组
{A,B,C}
。
9.7.12
字符串截取函数
fn:substring
函数
fn:substring
函数用于截取字符串。它的参数、返回结果和描述如表
9.28
所示:
表
9.28
fn:substring
函数
|
参数
|
描述
|
|
string
|
源字符串。其类型必须为
String
类型
|
|
beginIndex
|
指定起始下标(值从
0
开始)。其类型必须为
int
类型
|
|
endIndex
|
指定结束下标(值从
0
开始)。其类型必须为
int
类型
|
|
返回结果
|
返回一个
String
类型的值
|
下面看一个示例。
${fn:substring("ABC","1","2")}<br>
截取结果为“
B
”。
9.7.14
起始到定位截取字符串函数
fn:substringBefore
函数
fn:substringBefore
函数允许截取源字符从开始到某个字符串。它的参数和
fn:substringAfter
函数相同,不同的是
substring
表示的是结束字符串。下面看一个示例。
${fn:substringBefore("ABCD","BC")}<br>
截取的结果为“
A
”。
9.7.15
小写转换函数
fn:toLowerCase
函数
fn:toLowerCase
函数允许将源字符串中的字符全部转换成小写字符。它只有一个表示源字符串的参数
string
,函数返回一个
String
类型的值。下面看一个示例。
${fn:toLowerCase("ABCD")}<br>
转换的结果为“
abcd
”。
9.7.16
大写转换函数
fn:toUpperCase
函数
fn:toUpperCase
函数允许将源字符串中的字符全部转换成大写字符。它与
fn:toLowerCase
函数相同,也只有一个
String
参数,并返回一个
String
类型的值。下面看一个示例。
${fn:toUpperCase("abcd")}<br>
转换的结果为“
ABCD
”。
9.7.17
空格删除函数
fn:trim
函数
fn:trim
函数将删除源字符串中结尾部分的“空格”以产生一个新的字符串。它与
fn:toLowerCase
函数相同,只有一个
String
参数,并返回一个
String
类型的值。下面看一个示例。
${fn:trim("AB C ")}D<br>
转换的结果为“
AB CD
”,注意,它将只删除词尾的空格而不是全部,因此“
B
”和“
C
”之间仍然留有一个空格。
Database access
标签库中的标签用来提供在
JSP
页面中可以与数据库进行交互的功能,虽然它的存在对于早期纯
JSP
开发的应用以及小型的开发有着意义重大的贡献,但是对于
MVC
模型来说,它却是违反规范的。因为与数据库交互的工作本身就属于业务逻辑层的工作,所以不应该在
JSP
页面中出现,而是应该在模型层中进行。
对于
Database access
标签库本书不作重点介绍,只给出几个简单示例让读者略微了解它们的功能。
Database access
标签库有以下
6
组标签来进行工作:
<sql:setDataSource>
、
<sql:query>
、
<sql:update>
、
<sql:transaction>
、
<sql:setDataSource>
、
<sql:param>
、
<sql:dateParam>
。
9.6.1
用于设置数据源的
<sql:setDataSource>
标签
<sql:setDataSource>
标签用于设置数据源,下面看一个示例:
<sql:setDataSource
var="dataSrc"
url="jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/myDB"
driver="org.postgresql.Driver"
user="admin"
password="1111"/>
该示例定义一个数据源并保存在“
dataSrc
”变量内。
9.6.2
用于查询的
<sql:query>
标签
<sql:query>
标签用于查询数据库,它标签体内可以是一句查询
SQL
。下面看一个示例:
<sql:query var="queryResults" dataSource="${dataSrc}">
select * from table1
</sql:query>
该示例将返回查询的结果到变量“
queryResults
”中,保存的结果是
javax.servlet.jsp.jstl.sql.Result
类型的实例。要取得结果集中的数据可以使用
<c:forEach>
循环来进行。下面看一个示例。
<c:forEach var="row" items="${queryResults.rows}">
<tr>
<td>${row.userName}</td>
<td>${row.passWord}</td>
</tr>
</c:forEach>
“
rows
”是
javax.servlet.jsp.jstl.sql.Result
实例的变量属性之一,用来表示数据库表中的“列”集合,循环时,通过“
${row.XXX}
”表达式可以取得每一列的数据,“
XXX
”是表中的列名。
9.6.3
用于更新的
<sql:update>
标签
<sql:update>
标签用于更新数据库,它的标签体内可以是一句更新的
SQL
语句。其使用和
<sql:query>
标签没有什么不同。
9.6.4
用于事务处理的
<sql:transaction>
标签
<sql:transaction>
标签用于数据库的事务处理,在该标签体内可以使用
<sql:update>
标签和
<sql:query>
标签,而
<sql:transaction>
标签的事务管理将作用于它们之上。
<sql:transaction>
标签对于事务处理定义了
read_committed
、
read_uncommitted
、
repeatable_read
、
serializable4
个隔离级别。
9.6.5
用于事务处理的
<sql:param>
、
<sql:dateParam>
标签
这两个标签用于向
SQL
语句提供参数,就好像程序中预处理
SQL
的“
?
”一样。
<sql:param>
标签传递除
java.util.Date
类型以外的所有相融参数,
<sql:dateParam>
标签则指定必须传递
java.util.Date
类型的参数。
看到
I18N
就应该想到知识“国际化”,
I18N formatting
标签库就是用于在
JSP
页面中做国际化的动作。在该标签库中的标签一共有
12
个,被分为了两类,分别是:
q
国际化核心标签:
<fmt:setLocale>
、
<fmt:bundle>
、
<fmt:setBundle>
、
<fmt:message>
、
<fmt:param>
、
<fmt:requestEncoding>
。
q
格式化标签:
<fmt:timeZone>
、
<fmt:setTimeZone>
、
<fmt:formatNumber>
、
<fmt:parseNumber>
、
<fmt:formatDate>
、
<fmt:parseDate>
。
下面只选择其中常见的一些标签和属性进行介绍。
9.5.1
用于设置本地化环境的
<fmt:setLocale>
标签
<fmt:setLocale>
标签用于设置
Locale
环境。它的属性和描述如表
9.17
所示:
表
9.17
<fmt:setLocale>
标签属性和说明
|
属性
|
描述
|
|
value
|
Locale
环境的指定,可以是
java.util.Locale
或
String
类型的实例
|
|
scope
|
Locale
环境变量的作用范围(可选)
|
下面看一个示例:
<fmt:setLocale value="zh_TW"/>
表示设置本地环境为繁体中文。
9.5.2
用于资源文件绑定的
<fmt:bundle>
、
<fmt:setBundle>
标签
这两组标签用于资源配置文件的绑定,唯一不同的是
<fmt:bundle>
标签将资源配置文件绑定于它标签体中的显示,
<fmt:setBundle>
标签则允许将资源配置文件保存为一个变量,在之后的工作可以根据该变量来进行。
根据
Locale
环境的不同将查找不同后缀的资源配置文件,这点在国际化的任何技术上都是一致的,通常来说,这两种标签单独使用是没有意义的,它们都会与
I18N formatting
标签库中的其他标签配合使用。它们的属性和描述如表
9.18
所示:
表
9.18
<fmt:bundle>
、
<fmt:setBundle>
标签属性和说明
|
属性
|
描述
|
|
basename
|
资源配置文件的指定,只需要指定文件名而无须扩展名,二组标签共有的属性
|
|
var
|
<fmt:setBundle>
独有的属性,用于保存资源配置文件为一个变量
|
|
scope
|
变量的作用范围
|
下面看一个示例
<fmt:setLocale value="zh_CN"/>
<fmt:setBundle basename="applicationMessage" var="applicationBundle"/>
该示例将会查找一个名为
applicationMessage_zh_CN.properties
的资源配置文件,来作为显示的
Resource
绑定。
9.5.3
用于显示资源配置文件信息的
<fmt:message>
标签
用于信息显示的标签,将显示资源配置文件中定义的信息。它的属性和描述如表
9.19
所示:
表
9.19
<fmt:message>
标签属性和说明
|
属性
|
描述
|
|
key
|
资源配置文件的“键”指定
|
|
bundle
|
若使用
<fmt:setBundle>
保存了资源配置文件,该属性就可以从保存的资源配置文件中进行查找
|
|
var
|
将显示信息保存为一个变量
|
|
scope
|
变量的作用范围
|
下面看一个示例:
<fmt:setBundle basename="applicationMessage" var="applicationBundle"/>
<fmt:bundle basename="applicationAllMessage">
<fmt:message key="userName" />
<p>
<fmt:message key="passWord" bundle="${applicationBundle}" />
</fmt:bundle>
该示例使用了两种资源配置文件的绑定的做法,“
applicationMessage
”资源配置文件利用
<fmt:setBundle>
标签被赋于了变量“
applicationBundle
”,而作为
<fmt:bundle>
标签定义的“
applicationAllMessage
”资源配置文件作用于其标签体内的显示。
q
第一个
<fmt:message>
标签将使用“
applicationAllMessage
”资源配置文件中“键”为“
userName
”的信息显示。
q
第二个
<fmt:message>
标签虽然被定义在
<fmt:bundle>
标签体内,但是它使用了
bundle
属性,因此将指定之前由
<fmt:setBundle>
标签保存的“
applicationMessage
”资源配置文件,该“键”为“
passWord
”的信息显示。
9.5.4
用于参数传递的
<fmt:param>
标签
<fmt:param>
标签应该位于
<fmt:message>
标签内,将为该消息标签提供参数值。它只有一个属性
value
。
<fmt:param>
标签有两种使用版本,一种是直接将参数值写在
value
属性中,另一种是将参数值写在标签体内。
9.5.6
用于为请求设置字符编码的
<fmt:requestEncoding>
标签
<fmt:requestEncoding>
标签用于为请求设置字符编码。它只有一个属性
value
,在该属性中可以定义字符编码。
9.5.7
用于设定时区的
<fmt:timeZone>
、
<fmt:setTimeZone>
标签
这两组标签都用于设定一个时区。唯一不同的是
<fmt:timeZone>
标签将使得在其标签体内的工作可以使用该时区设置,
<fmt:setBundle>
标签则允许将时区设置保存为一个变量,在之后的工作可以根据该变量来进行。它们的属性和描述如表
9.20
所示:
表
9.20
<fmt:timeZone>
、
<fmt:setTimeZone>
标签
属性和说明
|
属性
|
描述
|
|
value
|
时区的设置
|
|
var
|
<fmt:setTimeZone>
独有的属性,用于保存时区为一个变量
|
|
scope
|
变量的作用范围
|
9.5.8
用于格式化数字的
<fmt:formatNumber>
标签
<fmt:
formatNumber
>
标
签用于格式化数字。它的属性和描述如表
9.21
所示:
表
9.21
<fmt:formatNumber>
标签属性和说明
|
属性
|
描述
|
|
value
|
格式化的数字,该数值可以是
String
类型或
java.lang.Number
类型的实例
|
|
type
|
格式化的类型
|
|
pattern
|
格式化模式
|
|
var
|
结果保存变量
|
|
scope
|
变量的作用范围
|
|
maxIntegerDigits
|
指定格式化结果的最大值
|
|
minIntegerDigits
|
指定格式化结果的最小值
|
|
maxFractionDigits
|
指定格式化结果的最大值,带小数
|
|
minFractionDigits
|
指定格式化结果的最小值,带小数
|
<fmt:formatNumber>
标签实际是对应
java.util.NumberFormat
类,
type
属性的可能值包括
currency
(货币)、
number
(数字)和
percent
(百分比)。
下面看一个示例。
<fmt:formatNumber value="1000.888" type="currency" var="money"/>
该结果将被保存在“
money
”变量中,将根据
Locale
环境显示当地的货币格式。
9.5.9
用于解析数字的
<fmt:parseNumber>
标签
<fmt:parseNumber>
标签用于解析一个数字,并将结果作为
java.lang.Number
类的实例返回。
<fmt:parseNumber>
标签看起来和
<fmt:formatNumber>
标签的作用正好相反。它的属性和描述如表
9.22
所示:
表
9.22
<fmt:parseNumber>
标签属性和说明
|
属性
|
描述
|
|
value
|
将被解析的字符串
|
|
type
|
解析格式化的类型
|
|
pattern
|
解析格式化模式
|
|
var
|
结果保存变量,类型为
java.lang.Number
|
|
scope
|
变量的作用范围
|
|
parseLocale
|
以本地化的形式来解析字符串,该属性的内容应为
String
或
java.util.Locale
类型的实例
|
下面看一个示例。
<fmt:parseNumber value="15%" type="percent" var="num"/>
解析之后的结果为“
0.15
”。
9.5.10
用于格式化日期的
<fmt:formatDate>
标签
<fmt:formatDate>
标签用于格式化日期。它的属性和描述如表
9.23
所示:
表
9.23
<fmt:formatDate>
标签属性和说明
|
属性
|
描述
|
|
value
|
格式化的日期,该属性的内容应该是
java.util.Date
类型的实例
|
|
type
|
格式化的类型
|
|
pattern
|
格式化模式
|
|
var
|
结果保存变量
|
|
scope
|
变量的作用范围
|
|
timeZone
|
指定格式化日期的时区
|
<fmt:formatDate>
标签与
<fmt:timeZone>
、
<fmt:setTimeZone>
两组标签的关系密切。若没有指定
timeZone属性,
也可以通过
<fmt:timeZone>
、
<fmt:setTimeZone>
两组标签设定的时区来格式化最后的结果。
9.5.11
用于解析日期的
<fmt:parseDate>
标签
<fmt:parseDate>
标签用于解析一个日期,并将结果作为
java.lang.Date
类型的实例返回。
<fmt:parseDate>
标签看起来和
<fmt:formatDate>
标签的作用正好相反。它的属性和描述如表
9.24
所示:
表
9.24
<fmt:parseDate>
标签属性和说明
|
属性
|
描述
|
|
value
|
将被解析的字符串
|
|
type
|
解析格式化的类型
|
|
pattern
|
解析格式化模式
|
|
var
|
结果保存变量,类型为
java.lang.Date
|
|
scope
|
变量的作用范围
|
|
parseLocale
|
以本地化的形式来解析字符串,该属性的内容为
String
或
java.util.Locale
类型的实例
|
|
timeZone
|
指定解析格式化日期的时区
|
<fmt:parseNumber>
和
<fmt:parseDate>
两组标签都实现解析字符串为一个具体对象实例的工作,因此,这两组解析标签对
var
属性的字符串参数要求非常严格。就
JSP
页面的表示层前段来说,处理这种解析本不属于份内之事,因此
<fmt:parseNumber>
和
<fmt:parseDate>
两组标签应该尽量少用,替代工作的地方应该在服务器端表示层的后段,比如在
Servlet
中。
摘要: 9.3.9
用于包含页面的
<c:import>
...
阅读全文
摘要: 9.3.2
用于赋值的
<c:set>
...
阅读全文
摘要: 9.2.3 EL
表达式的操作符
...
阅读全文
这是Jboss 的jBPM3.12框架的用户指南的中文翻译。我的翻译风格是中英文对照,只翻译部分我认为重要的,不翻译简单的英文,以免浪费你我的时间。 同时,对于其中的部分内容,我会在翻译中做出解释和写上我的理解。
Chapter 5. Deployment部署
jBPM is an embeddable BPM engine, which means that you can take jBPM and embed it into your own java project, rather then installing a separate product and integrate with it. One of the key aspects that make this possible is minimizing the dependencies. This chapter discusses the jbpm libraries and their dependencies.
jBPM是一个嵌入式的BPM(业务程序管理)引擎。本章讨论jbpm库和它的依赖库。
5.1. Java runtime environment
jBPM 3 requires J2SE 1.4.2+
5.2. jBPM libraries
jbpm-[version].jar is the library with the core jbpm functionality.是jbpm的核心功能库。
jbpm-identity-[version].jar is the (optional) library containing an identity component as described in Section 11.11, “The identity component”.
可选的,这个库包含了身份验证组件。用于流程的参与者的管理。
5.3. Third party libraries第三方库
In a minimal deployment, you can create and run processes with jBPM by putting only the commons-logging and dom4j library in your classpath. Beware that persisting processes to a database is not supported. The dom4j library can be removed if you don't use the process xml parsing, but instead build your object graph programatically.
最小的jbpm部署,只需要核心jbpm库和commons-logging库,以及dom4j库到你的classpath中。此时,不支持持久化业务程序到数据库。
Table 5.1.
Library库 | Usage用途 | Description描述 | Directory目录 |
commons-logging.jar | logging in jbpm and hibernate | The jBPM code logs to commons logging. The commons logging library can be configured to dispatch the logs to e.g. java 1.4 logging, log4j, ... See the apache commons user guide for more information on how to configure commons logging. if you're used to log4j, the easiest way is to put the log4j lib and a log4j.properties in the classpath. commons logging will automatically detect this and use that configuration. | lib/jboss (from jboss 4.0.3) |
dom4j-1.6.1.jar | process definitions and hibernate persistence | xml parsing | lib/dom4j |
A typical deployment for jBPM will include persistent storage of process definitions and process executions. In that case, jBPM does not have any dependencies outside hibernate and its dependent libraries.
典型的jBPM部署包括持久化业务程序定义和执行的功能。 需要Hibernate
Of course, hibernate's required libraries depend on the environment and what features you use. For details refer to the hibernate documentation. The next table gives an indication for a plain standalone POJO development environment.
下面的表给出了简单的标准POJO部署环境需要的第三方库。
jBPM is distributed with hibernate 3.1 final. But it can also work with 3.0.x. In that case, you might have to update a few hibernate queries in the hibernate.queries.hbm.xml configuration file. For more info about customizing queries, see Section 7.6, “Customizing queries”
Table 5.2.
Library库 | Usage | Description | Directory |
hibernate3.jar | hibernate persistence | the best O/R mapper | lib/hibernate (hibernate 3.1 final) |
antlr-2.7.5H3.jar | used in query parsing by hibernate persistence | parser library | lib/jboss (from jboss 4.0.3) |
cglib-2.1_2jboss.jar | hibernate persistence | reflection library used for hibernate proxies | lib/jboss (from jboss 4.0.3) |
commons-collections.jar | hibernate persistence | | lib/jboss (from jboss 4.0.3) |
ehcache-1.1.jar | hibernate persistence (in the default configuration) | second level cache implementation.二级缓存实现。 When configuring a different cache provider for hibernate, this library is not required. | lib/hibernate |
jaxen-1.1-beta-4.jar | process definitions and hibernate persistence | XPath library (used by dom4j) | lib/hibernate |
jdbc2_0-stdext.jar | hibernate persistence | | lib/hibernate |
asm.jar | hibernate persistence | asm byte code library 二进制代码修改库 | lib/hibernate |
asm-attrs.jar | hibernate persistence | asm byte code library | lib/hibernate |
The beanshell library is optional. If you don't include it, you won't be able to use the beanshell integration in the jbpm process language and you you'll get a log message saying that jbpm couldn't load the Script class and hence, the script element won't be available.
Beanshell库是可选的。
Table 5.3.
Library | Usage | Description | Directory |
bsh-1.3.0.jar | beanshell script interpreter | Only used in the script's and decision's. When you don't use these process elements, the beanshell lib can be removed, but then you have to comment out the Script.hbm.xml mapping line in the hibernate.cfg.xml | lib/jboss |
摘要: 这是Jboss 的jBPM3.12框架的用户指南的中文翻译。我的翻译风格是中英文对照,只翻译部分我认为重要的,不翻译简单的英文,以免浪费你我的时间。 同时,对于其中的部分内容,我会在翻译中做出解释和写上我的理解。
Chapter 4. Graph Oriented Programming面向图表编程4.1. Introduction介绍This chapter can be conside...
阅读全文
摘要: 这是Jboss 的jBPM3.12框架的用户指南的中文翻译。我的翻译风格是中英文对照,只翻译部分我认为重要的,不翻译简单的英文,以免浪费你我的时间。 同时,对于其中的部分内容,我会在翻译中做出解释和写上我的理解。Chapter 3. Tutorial指南This tutorial will show you basic process constructs 过程建造in jpdl an...
阅读全文
这是Jboss 的jBPM3.12框架的用户指南的中文翻译。我的翻译风格是中英文对照,只翻译部分我认为重要的,不翻译简单的英文,以免浪费你我的时间。
同时,对于其中的部分内容,我会在翻译中做出解释和写上我的理解。
Chapter 2. Getting started起步
This chapter takes you through the first steps of getting JBoss jBPM and provides the initial pointers to get up and running in no time.
初始化JBpm3.12
2.1. Downloadables Overview
Listed below are the different jBPM packages that are available today. Each of these packages contains one or more downloadable files. Along with each of these files goes a description of its contents and a pointer to any relevant installation instructions if they are available.
All downloads described below can be found on the sourceforge jbpm downloads page.
2.1.1. jBPM 3
Download JBoss jBPM 3 at sourceforge.net. This is the main distribution package containing the core engine and a number of additional modules that you may need to work with jBPM. 包括JBpm核心和其他包。
- The Starters Kit (jbpm-starters-kit-<version>.zip): If you want to get started with jBPM quickly, this is the file you want to download. It contains all the other modules of this package plus the graphical designer in one single download. Extract the zipped archive into a folder of your choice and read the file named 'readme.html' for more info and further installation instructions. With this starters kit you can immediately get started with the Chapter 3, Tutorial.
包含了包括图形化设计器在内的所有模块,能够帮助你快速启动。
- Core Engine and Identity Component (jbpm-<version>.zip): The download contains the jBPM core engine as well as the identity component for actor and group management. To start working with it, extract the archive into a folder of your choice. You will find pointers to the User's Guide and other important information resources in the 'readme.html' file in the 'jbpm-<version>' folder.
核心,包括核心引擎和身份组建,内有用户指南文档。
- Database Extensions (jbpm-db-<version>.zip):数据库扩展 The database extension pack contains the jBPM core engine as well as the identity component for actor and group management. To start working with it, extract the archive into a folder of your choice. You will find pointers to the User's Guide and other important information resources in the 'readme.html' file in the 'jbpm-<version>' folder.
2.1.2. jBPM Process Designer
jBPM过程设计器
Download JBoss jBPM Process Designer at sourceforge.net. The designer is an eclipse plugin and enables you to author 创作your process definitions过程定义 and to easily deploy them. The plug-in is available for download either as a zipped Eclipse feature or as a zipped Eclipse update site. There is no difference in content, the only difference is in the way you have to do the installation.
- Eclipse Update Site (jbpm-gpd-site-<version>.zip): If you want to be absolutely sure that the designer installation goes smoothly, we recommend to use the update site mechanism together with a new Eclipse installation. Of cource the Eclipse version should match the downloaded update site archive. To get started with the designer plugin, follow the instructions in the 'readme.html' file included in the archives root folder to succesfully install the GPD.
使用本地站点更新方式部署。
- Eclipse Feature (jbpm-gpd-feature-<version>.zip): If you are tired of each time having to do a fresh Eclipse installation and you are willing to cope with some possible issues, you can try the feature download. In this case installation is as easy as extracting the archive into your Eclipse installation (make sure the included 'plugins' and 'features' folders end up in the same location of your Eclipse installation) overwriting the files and folders with the same name that are possibly already present. This installation is very easy, but you could run into incompatibility issues when you overwrite plugins already present in your installation because of other features that you did install. Though they have the same name it could happen that the versions of these colliding plugins are not equal, hence the possible incompatibilities. The installation instructions are repeated in the 'readme.html' file.
这个是手工部署。
2.1.3. jBPM BPEL extension
Download JBoss jBPM BPEL extension at sourceforge.net. It contains only one file : jbpm-bpel-<version>.zip. To get started with the BPEL extensions, look in the User's Guide in the 'doc' subfolder of the toplevel folder.
jbpm-bpel:含有JBoss jBPM的BPEL扩展件方面的信息。
BPEL是一个规范的SOA组件。因为与JBoss jBPM使用的许可证不同,所以被独立了出来。
2.2. The JBoss jBPM project directory
- professional support: JBoss is the company that backs this project with professional support, training and consultancy services.
- user guide: is the document you're reading and serves as the main entry point into the project.
- forums: get in contact with the community, ask questions and discuss jBPM 论坛,社区。
- wiki: extra information, mostly provided by the community
- issue tracker: for submitting bugs and feature requests
- downloads: sourceforge download page for jBPM
- mailing lists: mailing lists are used for announcements
- javadocs: part of the download in the doc/javadoc directory.
2.3. CVS access
2.3.1. Anonymous CVS access
Alternatively, you can get JBoss jBPM from cvs with the following information:
- Connection type: pserver
- User: anonymous
- Host: anoncvs.forge.jboss.com
- Port: 2401 (which is the default)
- Repository path: /cvsroot/jbpm
- Label: :pserver:anonymous@anoncvs.forge.jboss.com:/cvsroot/jbpm
2.3.2. Developer CVS access
To get cvs developer access, you must sign contributors agreement and you need an ssh key. More information on both can be found on the JBoss cvs repository wiki page
- Connection type: ext over ssh (extssh in eclipse)
- User: sf.net username or jboss username
- Host: cvs.forge.jboss.com
- Port: 2401 (which is the default)
- Repository path: /cvsroot/jbpm
- Label: :pserver:anonymous@cvs.forge.jboss.com:/cvsroot/jbpm
利用JBPM开发一个工作流应用,相对于使用shark是比较简单直观的。我们之前提到过,一个工作流管理系统最基本的组件包括流程定义组件,流程执行组件和流程客户端组件。下面从这三个方面看一下JBPM对开发工组流应用的支持。
1.
流程的定义
JBPM
没有采用WfMC提出的流程定义语言XPDL,而是自己开发了一种称为JPDL的语言来定义流程。因此,在开发一个应用时我们最终需要生成一个符合该XML schema的文件processdefinition.xml来表示定义好的流程。它可以manually获得,也可以使用可视化的定义工具自动生成。
JBPM
专门提供了一个开发流程的环境,称为process development environment(pde)。可以
在
jbpm
根目录下执行命令
ant create.pde
来生成
pde
工作目录
。生成的包结构如下所示:

Build.xml
文件用于配置一个流程,即利
用
ant
工具解析
processdefinition.xml
文件,并将运行流程时所需的相关信息存储到数据库中。
Lib
存放了开发和配置流程所需的全部库文件,包括数据库的
jdbc
驱动。
Src
包括开发和配置流程的全部源文件和所需资源。
Src/config
只有两个文件,
jbpm.properties
和
log4j.properties
。其中,
jbpm.propertie
文件包含了数据库的配置信息。因此,更换数据库或数据库的
jdbc
驱动都需要修改这里。
Scr/java
存放
java
源文件。
Src/process
存放工作流定义文件
(processdefinition.xml)
和相关的资源文件,如图片和
form
文件。
Src/test
存放测试代码。
Target/classes
是
src/java
中源码的输出目录,存放编译后的
class
文件。
Target/par
存放用命令
ant build.process.archives
生成的
par
包。
Par
包实际上就是把
src/process
中的流程定义及相关文件打包成
zip
形式存储。
Target/test-classes
存放测试程序的编译结果。
Target/test-report
存放测试报告。
2. 流程的执行
JBPM
把负责执行流程的类库打包成jbpm.core.jar,它也是JBPM工作流引擎的核心。在开发一个工作流应用时,只需将该jar文件放到相应的lib目录下面。而开发人员就可以专注于开发一个流程模型,完成对流程的定义,而无需过多考虑流程执行的细节。
3.
流程的客户端
客户端组件的开发,需要一个应用服务器作为servlet container,我们这里选择了tomcat。JBPM将开发一个webapp所需的类打包成jbpm.web.jar,包括自定义的tag和Struts用到的类等等。开发应用时,将该jar放到WEB-INF\lib下面就可以了。
一个基于工作流的webapp应用的开发和普通webapp的开发方式很相似。包结构也保持一贯作风:

所以,我们需要做的主要工作是完成客户端应用所需的
jsp
页面的开发,可以选用
Struts
来进行开发。需要注意的是,我们要对
lib
目录下的
jbpm.properties
文件进行配置,主要是对数据库
jdbc
驱动的配置。
4.
系统数据库的创建
JBPM
可以支持多种数据库系统,包括MSSQL,,Mysql,Oracle,hdbsql等。它提供了很灵活的配置方式,只需要修改jbpm.properties文件,同时将相应的JDBC Driver拷贝到lib目录就可以了。利用ant的generate.ddl命令,JBPM还支持自动生成用于创建系统表的sql脚本,而且可以生成对应于各种数据库系统的脚本,非常便于数据库系统的更换和系统数据库的创建。
5. 开发过程
环境配置如下:
JBPM 2.0
Ant 1.6.2
Tomcat 5.0.27
SQL Server 2000
SQL Server 2000 Driver for JDBC
仍以之前演示过的request a payraise为例(见下图),介绍一下利用JBPM开发一个工作流应用需要完成的工作。

1)
首先,我们需要完成流程的定义。这不仅包括定义processdefinition.xml,还要对流程执行时使用到的其他资源进行定义。比如,在web应用中用到的图片,form等。还需要配置form.xml,该文件确定了流程中不同状态和form的关系,如request a payraise状态下,需要如下图所示的form:

补充Processdefinition.xml
示例:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE process-definition PUBLIC "-//jBpm/jBpm Mapping DTD 2.0//EN" "http://jbpm.org/dtd/processdefinition-2.0.dtd">
<process-definition name="pay raise process">
<!-- SWIMLANES -->
<swimlane name="requester" />
<swimlane name="boss">
<delegation class="org.jbpm.delegation.assignment.ActorAssignmentHandler">cg</delegation>
</swimlane>
<swimlane name="erp operator">
<delegation class="org.jbpm.delegation.assignment.ActorAssignmentHandler">pf</delegation>
</swimlane>
<!-- START-STATE -->
<start-state name="request a payraise" swimlane="requester">
<transition to="evaluating"/>
</start-state>
<!-- NODES -->
<state name="evaluating">
<assignment swimlane="boss" />
<transition name="approve" to="fork"/>
<transition name="disapprove" to="done"/>
</state>
<fork name="fork">
<transition to="updating erp asynchronously" />
<transition to="treating collegues on cake and pie" />
</fork>
<state name="updating erp asynchronously">
<assignment swimlane="erp operator" />
<transition to="join" />
</state>
<state name="treating collegues on cake and pie">
<assignment swimlane="requester" />
<transition to="join" />
</state>
<join name="join">
<transition to="done" />
</join>
<!-- END-STATE -->
<end-state name="done" />
</process-definition>
2)
有了processdefinition.xml文件,我们就可以配置流程。即使用ant命令,解析这个文件并且将执行时需要的信息存储在数据库中。如下图:

3)
我们无需关心流程将怎么执行,完全交给jbpm.core.jar就好。
4)
剩下的另外一项比较繁重的工作就是开发一个用于该流程的客户端应用。前面已经提到过,
我们需要做的主要工作是完成客户端应用所需的
jsp
页面的开发。包括登录页面,查看自己的
tasklist
页面,执行
task
的页面等。除此之外,还可以通过日志来完成流程的监控和管理界面。这些都由应用的需求来决定。
这是Jboss 的jBPM3.12框架的用户指南的中文翻译。其中第一章的译文,是我在网上找到的。其他几章都是我自己做的翻译。我的翻译是中英文对照,只翻译部分我认为重要的,不翻译简单的英文,以免浪费你我的时间。
同时,对于其中的部分内容,我会在翻译中做出解释。
下面是从网络上找到的第一章,这是jBPM3.0的用户指南的译文。但是第一章,3.0和3.1内容相差不大,我就不做翻译了。直接使用这一篇。
目录
第一章绪论
JBoss jBPM 是一个灵活的,易扩展的工作流管理系统。JBoss jBPM有一套直观的流程建模语言,这套语言能用任务(task),异步通信的等待状态(wait state ),定时器(timer),自动化的动作(automated action)等来图形化的表示业务流程。为了把这些操作集成在一
起,JBoss jBPM拥有强大的,易扩展的控制流程机制。
JBoss jBPM对外依赖程度很小,你完全可以像用java的类库一样用它。并且它也可以被部署在高性能的J2EE集群应用服务器上。
JBoss jBPM能配置在任何数据库上,并且能被部署在任何的应用服务器上。
1.1 总览
工作流和业务流程处理功能的核心部分被打包成一个简单的java类库。这个类库包括了这样一个服务:流程信息的存储,更新,和从数据库中重新取回。
图1.1:JBoss jBPM组成模块的概略图
1.2 JBoss jBPM starter kit
starter kit是一个包含jbpm所有模块的下载包。这个下载包中包括以下模块:
· jbpm-server, 一个预选配置好的jboss应用服务器。
· jbpm-designer, 图形化定制流程的eclipse插件。
· jbpm-db, jBPM的数据库兼容包 (见后边论述)。
· jbpm, jbpm的核心模块,其中包括libs文件夹和这个用户说明。
· jbpm-bpel, JBoss jBPM对BPEL扩展的一些参考资料
预先配置好的JBoss应用服务器具有如下组成部分:
jBPM核心模块,被打包成一个用于提供服务的存档文件
带有jbpm表的集成数据库:默认的hypersonic数据库拥有jbpm表,并且这个表已经拥有一个流程了。
Jbpm的web控制台,它既可以被Jbpm管理员用也可以被流程的参与者使用。
执行定时器的Jbpm的调度程序,这个调度程序在starter kit里边被配置成一个servlet。这个servlet会产生一个新的线程来监视和执行定时器。
一个具体流程的例子,它已经被部署在jbpm数据库中了。
1.3 JBoss jBPM 流程图形定制器
JBoss jBPM还拥有一套图形化的设计工具。这个设计器是一个图形化的业务流程定制工具。
JBoss jBPM流程图形定制器是eclipse的一个插件。单独安装这个定制器非常简单。
这个图形设计器最重要的特性是:业务分析人员也能像技术开发人员一样用它来完成任务。这使得业务流程建模能平滑的转换到具体技术实现。
这个插件可以利用eclipse的一般升级机制通过一个升级站点得到安装(zip文件格式)。也可以通过解压一个特定的包到eclipse的安装目录来安装此插件。
1.4 JBoss jBPM的核心模块
JBoss jBPM的核心模块是一个用来管理流程定义和流程实例的执行环境的普通java程序。
JBoss jBPM是一个java类库。所以它可以被用在任何java环境中,比如:web应用程序,swing应用程序,EJB,web service……。JBPM类库还可以被打包并被当成无状态会话EJB(stateless session EJB)使用。这样可使它被部署在集群上并且适应高性能应用。这些无状态会话EJB必须符合J2EE1.3规范这样才能使它可以被部署在任何应用服务器上。
JBoss jBPM的核心模块被打包成一个简单的java库文件。依你功能的需要,jbpm-3.0.jar这个库文件对一些第三方的类库比如hibernate, dom4j有所依赖。这些依赖在第五章(部署)中作了详细的说明。
至于持久化,JBPM在内部用了hibernate。除了传统的O/R映射功能,hibernate还解决了不同数据SQL dialect差异的问题,这使得JBPM能适应现在所有的数据库。
JBoss jBPM API可以被你工程中任何的java代码调用,比如,你的web应用程序,EJB,web service 模块,消息驱动bean或其它任何java模块。
1.5 JBoss jBPM web应用程序的控制台
jBPM web应用程序的控制台提供两种服务。首先,它被用来当作一个用来和流程执行过程中产生的任务进行交互的主要用户接口,其次,它还是一个用来检查和操作运行实例的管理和监控平台。
1.6 JBoss jBPM人员组织模块
JBoss jBPM可以和任何包括人员和其他组织信息的公司结构集成在一起。但是对那些组织结构信息模块很难获取的项目,JBoss jBPM提供了这个模块。这个模块使用的模型要比传统的servlet, ejb,portlet模型丰富的多。
更多信息,请参照第九章第九节人员组织模块
1.7 JBoss jBPM调度程序
JBoss jBPM调度程序是一个用来监测和执行在流程执行过程中设置的定时器的模块。
定时器模块被打包在jbpm的核心包中,但是它必须被部署在以下环境中:或者你必须订制一个调度servlet,它来产生一个监测线程,或者你必须启动一个单独的JVM来执行调度程序。
1.8 JBoss jBPM 数据库兼容包
JBoss jBPM 数据库兼容包是一个下载包,它包括所有的资料,drivers和scripts,用这些你可以使jbpm运行在你选择的数据库上。
1.9 JBoss jBPM BPE的扩展
JBoss jBPM BPE的扩展是一个为了支持BPEL独立的扩展包。BPEL的本质就是一组用来参照别的web service写web service的xml脚本语言。