现在流行抱大腿,不过对眼光的要求也高。要不就如高也,即使四眼,一样无用。对Java企业开发而言,Spring的腿则是一定要抱的。而所谓抱Spring的腿,无外乎三点:
一是通过Spring暴露出服务,将服务配置到Spring的IOC容器里;
二是在自己的运行环境里访问到Spring的IOC容器,能够轻松使用Spring容器里所配置的服务;
三是对于具有事务管理特性的项目来说,将事务管理与Spring的事务管理进行合并。
下面分别讨论:
一、 通过Spring暴露服务
还记得在jBPM4的运行期环境里提到的JbpmConfiguration吗?它是整个jBPM4的入口,并且是整个应用独此一份的。通过它可以获取processEngine,并藉此获得工作流引擎所提供的各种服务:
ProcessEngine processEngine = new Configuration()
.buildProcessEngine();
RepositoryService repositoryService = processEngine.getRepositoryService();
ExecutionService executionService = processEngine.getExecutionService();
TaskService taskService = processEngine.getTaskService();
HistoryService historyService = processEngine.getHistoryService();
ManagementService managementService = processEngine.getManagementService();
通过Spring暴露这些服务,配置如下:
<bean id="jbpmConfiguration" class="org.jbpm.pvm.internal.cfg.SpringConfiguration">
<constructor-arg value="be/inze/spring/demo/jbpm.cfg.xml" />
</bean>
<bean id="processEngine" factory-bean="jbpmConfiguration" factory-method="buildProcessEngine" />
<bean id="repositoryService" factory-bean="processEngine" factory-method="getRepositoryService" />
<bean id="executionService" factory-bean="processEngine" factory-method="getExecutionService" />
细心的你会发现,配置时使用了JbpmConfiguration 的子类SpringConfiguration。SpringConfiguration相比JbpmConfiguration有哪些增强呢,下面再讲。总之,现在,就可以使用Spring来获取或注入这些Jbpm4所提供的服务了。
二、在environment里加入SpringContext
jBPM4的environment(运行期环境)提供Engine IOC(process-engine-context)和Transaction IOC(transaction-context)。要想在运行期方便地访问到Spring里所配置的服务,最直接的方法就是在environment里加入Spring IOC(applicationContext)的引用。
SpringConfiguration即是对JbpmConfiguration增强了对Spring IOC的一个引用。
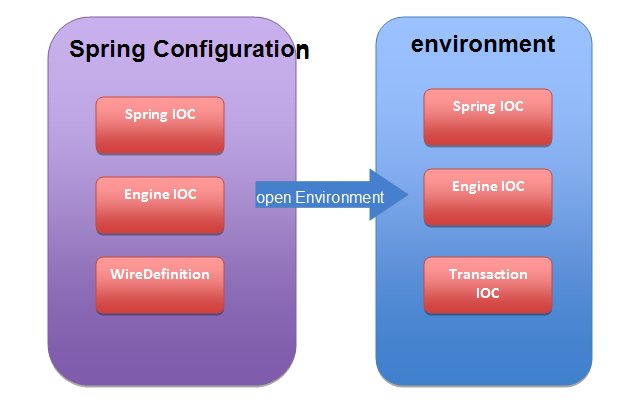
SpringConfiguration是如何做到的呢?简单,实现Spring的ApplicationContextAware接口,自动持有applicationContext,然后openEnvironment时将其加入environment。
environment.setContext(new SpringContext(applicationContext));
SpringContext是对applicationContext的简单封装。
那么什么从Engine IOC移民到Spring IOC了呢?是的,最重要的就是Hibernate Session Factory。
在jbpm.cfg.xml的process-engine-context里干掉:
<hibernate-configuration>
<cfg resource="jbpm.hibernate.cfg.xml" />
</hibernate-configuration>
<hibernate-session-factory />
相关配置挪动至Spring配置文件。
三、 事务
哪里有数据库操作,哪里就有事务。对于嵌入式工作流而言,最重要的集成就是事务的集成。这里先分析jBPM4的事务实现,然后再介绍集成入Spring的事务实现。
1、 Command模式
jBPM4的逻辑实现采用了Command模式。

采用Command模式后,jBPM4对CommandService构造拦截器(Interceptor)链,配置在jbpm.cfg.xml的process-engine-context里:
<command-service>
<retry-interceptor />
<environment-interceptor />
<standard-transaction-interceptor />
</command-service>
2、 原有的事务实现
jBPM4原有的事务通过StandardTransactionInterceptor实现,在CommandService执行Command之前打开事务(实际委派Hibernate的事务管理),完成后提交/回滚。

jBPM4的事务是基于Command的。
3、 集成入Spring的事务实现
Spring的事务是基于服务调用的。
使jBPM4使用Spring提供的事务:
<command-service>
<retry-interceptor />
<environment-interceptor />
<spring-transaction-interceptor current="true" />
</command-service>
拦截器换用SpringTransactionInterceptor,SpringTransactionInterceptor从environment 提供的Spring IOC获取PlatformTransactionManager,使用事务模板回调Command,事务传播模式强制加入当前事务。
同时,对hibernate session的配置(jbpm.cfg.xml的transaction-context)强制从当前线程中获取:
<hibernate-session current="true"/>
并干掉原有的事务实现:
<transaction />
参考文档:
http://www.slideshare.net/guest8d4bce/spring-integration-with-jbpm4
http://www.blogjava.net/ronghao 荣浩原创