参考 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Command_pattern
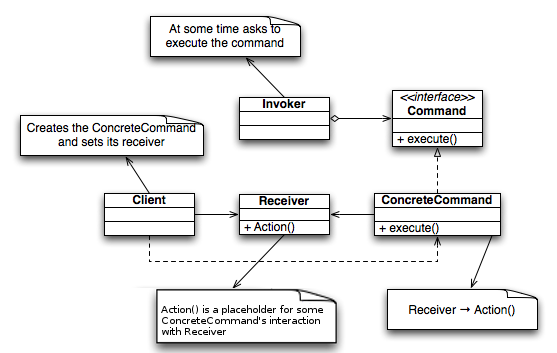
/*the Invoker class*/
public class Switch {
private Command flipUpCommand;
private Command flipDownCommand;
public Switch(Command flipUpCmd, Command flipDownCmd) {
this.flipUpCommand = flipUpCmd;
this.flipDownCommand = flipDownCmd;
}
public void flipUp() {
flipUpCommand.execute();
}
public void flipDown() {
flipDownCommand.execute();
}
}
/*Receiver class*/
public class Light {
public Light() { }
public void turnOn() {
System.out.println("The light is on");
}
public void turnOff() {
System.out.println("The light is off");
}
}
/*the Command interface*/
public interface Command {
void execute();
}
/*the Command for turning on the light*/
public class FlipUpCommand implements Command {
private Light theLight;
public FlipUpCommand(Light light) {
this.theLight=light;
}
public void execute(){
theLight.turnOn();
}
}
/*the Command for turning off the light*/
public class FlipDownCommand implements Command {
private Light theLight;
public FlipDownCommand(Light light) {
this.theLight=light;
}
public void execute() {
theLight.turnOff();
}
}
/*The test class or client*/
public class PressSwitch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Light lamp = new Light();
Command switchUp = new FlipUpCommand(lamp);
Command switchDown = new FlipDownCommand(lamp);
// See criticism of this model above:
// The switch itself should not be aware of lamp details (switchUp, switchDown)
// either directly or indirectly
Switch s = new Switch(switchUp,switchDown);
try {
if (args[0].equalsIgnoreCase("ON")) {
s.flipUp();
} else if (args[0].equalsIgnoreCase("OFF")) {
s.flipDown();
} else {
System.out.println("Argument \"ON\" or \"OFF\" is required.");
}
} catch (Exception e){
System.out.println("Arguments required.");
}
}
}
=====================
java tip (http://www.javaworld.com/javaworld/javatips/jw-javatip68.html?page=3) 给了类似的例子,多了Fan作为receiver:
TestCommand.java
class Fan {
public void startRotate() {
System.out.println("Fan is rotating");
}
public void stopRotate() {
System.out.println("Fan is not rotating");
}
}
class Light {
public void turnOn( ) {
System.out.println("Light is on ");
}
public void turnOff( ) {
System.out.println("Light is off");
}
}
class Switch {
private Command UpCommand, DownCommand;
public Switch( Command Up, Command Down) {
UpCommand = Up; // concrete Command registers itself with the invoker
DownCommand = Down;
}
void flipUp( ) { // invoker calls back concrete Command, which executes the Command on the receiver
UpCommand . execute ( ) ;
}
void flipDown( ) {
DownCommand . execute ( );
}
}
class LightOnCommand implements Command {
private Light myLight;
public LightOnCommand ( Light L) {
myLight = L;
}
public void execute( ) {
myLight . turnOn( );
}
}
class LightOffCommand implements Command {
private Light myLight;
public LightOffCommand ( Light L) {
myLight = L;
}
public void execute( ) {
myLight . turnOff( );
}
}
class FanOnCommand implements Command {
private Fan myFan;
public FanOnCommand ( Fan F) {
myFan = F;
}
public void execute( ) {
myFan . startRotate( );
}
}
class FanOffCommand implements Command {
private Fan myFan;
public FanOffCommand ( Fan F) {
myFan = F;
}
public void execute( ) {
myFan . stopRotate( );
}
}
public class TestCommand {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Light testLight = new Light( );
LightOnCommand testLOC = new LightOnCommand(testLight);
LightOffCommand testLFC = new LightOffCommand(testLight);
Switch testSwitch = new Switch( testLOC,testLFC);
testSwitch.flipUp( );
testSwitch.flipDown( );
Fan testFan = new Fan( );
FanOnCommand foc = new FanOnCommand(testFan);
FanOffCommand ffc = new FanOffCommand(testFan);
Switch ts = new Switch( foc,ffc);
ts.flipUp( );
ts.flipDown( );
}
}
Command.java
public interface Command {
public abstract void execute ( );
}