LEARN FROM:http://learn.akae.cn/media/ch31s03.html
1.变量
环境变量可以从父进程传给子进程,因此Shell进程的环境变量可以从当前Shell进程传给fork出来的子进程。用printenv命令可以显示当前Shell进程的环境变量.用set命令可以显示当前Shell进程中定义的所有变量(包括本地变量和环境变量)和函数.
本地变量:$ VARNAME=value 注意等号两边都不能有空格,否则会被Shell解释成命令和命令行参数。
子进程shell变量导出:$ export VARNAME=value 这样父进程的Shell也可以使用这个变量
2.通配符

ls ch[012][0-9].doc
3.命令代换
由反引号括起来的也是一条命令,Shell先执行该命令,然后将输出结果立刻代换到当前命令行中。例如定义一个变量存放date命令的输出:
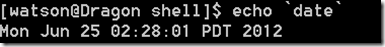
DATE=$(date)
4.算数代换
用于算术计算,$(())中的Shell变量取值将转换成整数
5.转义“\”
6.条件测试
7.控制
case
#! /bin/sh
echo "is it moring? Please answer yes or no ."
read YES_OR_NO
case "$YES_OR_NO" in
yes|Yes|y|YES)
echo "Good Moring!";;
[nN]*)
echo "Good afternoon.";;
*)
echo "Sorry, $YES_OR_NO not recognized. Enter yes or no . "
exit 1;;
esac
exit 0
for
#! /bin/sh
for FRUIT in apple banana pear ; do
echo "I like $FRUIT"
done
if
#! /bash/sh
echo "is it morning? please answer yes or no ."
read YES_OR_NO
if [ "$YES_OR_NO" = "yes" ]; then
echo "Good Morning."
elif [ "$YES_OR_NO" = "no" ]; then
echo "Good afternoon."
else
echo "Sorry ,$YES_OR_NO not recognized.Enter yes or no."
exit 1
fi
exit 0
While
#! /bin/sh
echo "Enter Password:"
read TRY
while [ "$TRY" != "p" ]; do
echo "Sorry, Try again"
read TRY
done
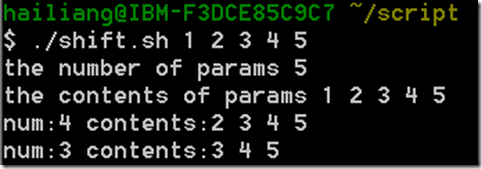
Shift
#! /bin/bash
echo "the number of params $#"
echo "the contents of params $@"
shift
echo "$1"
shift
echo "$1"
shift
echo "$1"
shift 向左偏移 ,$#代表传进参数的个数 而$@是具体的内容,当执行shift的时候,$#和$@也会相应的改变。
#! /bin/bash
echo "the number of params $#"
echo "the contents of params $@"
shift
echo "num:$# contents:$@"
shift
echo "num:$# contents:$@"
8.函数
#! /bin/sh
is_d()
{ DIR_NAME=$1
if ( test -d $DIR_NAME ); then
return 1
else
return 0
fi
}
for DIR in "$@" ; do
if is_d "$DIR"
then :
else
echo "not a dir"
fi
done
9.调试
Shell提供了一些用于调试脚本的选项,如下所示:
- -n
-
读一遍脚本中的命令但不执行,用于检查脚本中的语法错误
- -v
-
一边执行脚本,一边将执行过的脚本命令打印到标准错误输出
- -x
-
提供跟踪执行信息,将执行的每一条命令和结果依次打印出来
使用这些选项有三种方法,一是在命令行提供参数
set -x和
set +x分别表示启用和禁用
-x参数,这样可以只对脚本中的某一段进行跟踪调试。
从今天的一些编码来看,Shell编程要注意脚本中的空格,在if,while语句中 “[ ]”要留空格,以及变量的定义中,等号两端不要存有空格。